Data set on G4 DNA interactions with human proteins
- PMID: 29896522
- PMCID: PMC5996148
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.02.081
Data set on G4 DNA interactions with human proteins
Abstract
Guanine-rich DNA/RNA fragments can fold into G-quadruplexes (G4s) - non-canonical four-strand secondary structures. The article contains data on quadruplex interaction with human proteins. Binding of three topologically different G4 structures to more than 9000 human proteins was analyzed. Physicochemical methods were used to verify the results.The dataset was generated to identify the protein targets for DNA quadruplex structures for the purpose of better understanding the role of the structures in gene expression regulation. Presented data include functional interpretation of obtained gene lists, visualized with Cytoscape.
Figures



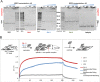








References
-
- Sekridova A.V., Varizhuk A.M., Tatarinova O.N., Severov V.V., Barinov N.A., Smirnov I.P., Lazarev V.N., Klinov D.V., Pozmogova G.E. Conformational polymorphysm of G-rich fragments of DNA Alu-repeats. I. Noncanonical structures. Biochem. (Mosc.) Suppl. Ser. B: Biomed. Chem. 2017;11(1):62–71. - PubMed
-
- Varizhuk M., Sekridova A.V., Tankevich M.V., Podgorsky V.S., Smirnov I.P., Pozmogova G.E. Conformational polymorphysm of G-rich fragments of DNA Alu-repeats. II. The putative role of G-quadruplex structures in genomic rearrangements. Biochem. (Mosc.) Suppl. Ser. B: Biomed. Chem. 2017;11(2):146–153. - PubMed
-
- Varizhuk D., Ischenko V., Tsvetkov R., Novikov N., Kulemin D., Kaluzhny M., Vlasenok V., Naumov I., Smirnov G. Pozmogova, The expanding repertoire of G4 DNA structures. Biochimie. 2017;135:54–62. - PubMed
-
- ThermoFisher Scientific, Protoarray Services. 〈https://www.thermofisher.com/ru/en/home/life-science/protein-biology/pr... (Accessed 18 January 2018).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

