Early femoral condyle insufficiency fractures after total knee arthroplasty: treatment with delayed surgery and femoral component revision
- PMID: 29896563
- PMCID: PMC5994640
- DOI: 10.1016/j.artd.2018.02.013
Early femoral condyle insufficiency fractures after total knee arthroplasty: treatment with delayed surgery and femoral component revision
Abstract
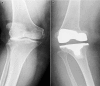
Background: Periprosthetic fracture following total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is usually associated with a traumatic event and typically treated with fracture fixation techniques. However, we report on a series of patients with early atraumatic condyle fractures that occurred as a result of insufficiency of the unloaded preoperative femoral condyle treated with delayed reconstruction.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed a series of 7 patients who sustained femoral condyle fractures following TKA and evaluated risk factors for insufficiency.
Results: There were 6 females and 1 male with an average age of 65.5 (range, 63-75) years and an average body mass index of 29.4 (range, 27-32). Fracture occurred on average 24.9 days from the index surgery and secondary to a low energy mechanism. Five patients had valgus alignment (mean, 15.2°) preoperatively and sustained fracture of the unloaded medial femoral condyle. Two patients had varus alignment (mean, 7.0°) preoperatively and both fractured the unloaded lateral condyle. One patient underwent early intervention requiring distal femoral replacement secondary to femoral bone loss. The remaining 6 patients underwent delayed surgery for an average of 6 weeks to allow for fracture healing followed by femoral component revision. At last follow-up (average, 48.5 months), 1 patient required a tibial component revision; however, no revision of the femoral component was required.
Conclusions: Early femoral condyle insufficiency fractures following TKA may be a risk in females with poor bone quality and preoperative valgus alignment. Delayed surgery and femoral component revision is a treatment strategy that prevented the need for other tertiary reconstruction.
Keywords: Delayed treatment; Insufficiency fracture; Periprosthetic fracture; Total knee arthroplasty.
Figures



References
-
- Berry D.J. Periprosthetic fractures after major joint replacement. Epidemiology: hip and knee. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999;30:183. - PubMed
-
- Healy W.L., Siliski J.M., Incavo S.J. Operative treatment of distal femoral fractures proximal to total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(1):27. - PubMed
-
- Rorabeck C.H., Taylor J.W. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur complicating total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999;30(2):265. - PubMed
-
- Merkel K.D., Johnson E.W., Jr. Supracondylar fracture of the femur after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68:29. - PubMed
-
- Ritter M.A., Faris P.M., Keating E.M. Anterior femoral notching and ipsilateral supracondylar femur fracture in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1988;3:185. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

