Transgenerational inheritance of chronic adolescent stress: Effects of stress response and the amygdala transcriptome
- PMID: 29896789
- PMCID: PMC6292780
- DOI: 10.1111/gbb.12493
Transgenerational inheritance of chronic adolescent stress: Effects of stress response and the amygdala transcriptome
Abstract
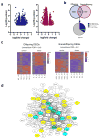
Adolescent stress can impact health and well-being not only during adulthood of the exposed individual but even in future generations. To investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying these long-term effects, we exposed adolescent males to stress and measured anxiety behaviors and gene expression in the amygdala-a critical region in the control of emotional states-in their progeny for two generations, offspring and grandoffspring. Male C57BL/6 mice underwent chronic unpredictable stress (CUS) for 2 weeks during adolescence and were used to produce two generations of offspring. Male and female offspring and grandoffspring were tested in behavioral assays to measure affective behavior and stress reactivity. Remarkably, transgenerational inheritance of paternal stress exposure produced a protective phenotype in the male, but not the female lineage. RNA-seq analysis of the amygdala from male offspring and grandoffspring identified differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in mice derived from fathers exposed to CUS. The DEGSs clustered into numerous pathways, and the "notch signaling" pathway was the most significantly altered in male grandoffspring. Therefore, we show that paternal stress exposure impacts future generations which manifest in behavioral changes and molecular adaptations.
Keywords: RNA-sequencing; adolescent stress; amygdala; chronic unpredictable stress; inheritance; multi-generational; notch signaling; stress; transcriptome; transgenerational.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons Ltd and International Behavioural and Neural Genetics Society.
Figures


References
-
- Gapp K, Bohacek J. Epigenetic germline inheritance in mammals: looking to the past to understand the future. Genes, Brain and Behavior. 2017 - PubMed
-
- Matthews SG, Phillips DI. Transgenerational inheritance of stress pathology. Experimental Neurology. 2012:95–101. - PubMed
-
- Franklin TB, et al. Epigenetic Transmission of the Impact of Early Stress Across Generations. Biological Psychiatry. 2010:408–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

