Progression-free survival at 24 months (PFS24) and subsequent outcome for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) enrolled on randomized clinical trials
- PMID: 29897404
- PMCID: PMC6096732
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdy203
Progression-free survival at 24 months (PFS24) and subsequent outcome for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) enrolled on randomized clinical trials
Abstract
Background: Patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with first-line anthracycline-based immunochemotherapy and remaining in remission at 2 years have excellent outcomes. This study assessed overall survival (OS) stratified by progression-free survival (PFS) at 24 months (PFS24) using individual patient data from patients with DLBCL enrolled in multi-center, international randomized clinical trials as part of the Surrogate Endpoint for Aggressive Lymphoma (SEAL) Collaboration.
Patients and methods: PFS24 was defined as being alive and PFS24 after study entry. OS from PFS24 was defined as time from identified PFS24 status until death due to any cause. OS was compared with each patient's age-, sex-, and country-matched general population using expected survival and standardized mortality ratios (SMRs).
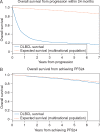
Results: A total of 5853 patients enrolled in trials in the SEAL database received rituximab as part of induction therapy and were included in this analysis. The median age was 62 years (range 18-92), and 56% were greater than 60 years of age. At a median follow-up of 4.4 years, 1337 patients (23%) had disease progression, 1489 (25%) had died, and 5101 had sufficient follow-up to evaluate PFS24. A total of 1423 assessable patients failed to achieve PFS24 with a median OS of 7.2 months (95% CI 6.8-8.1) after progression; 5-year OS after progression was 19% and SMR was 32.1 (95% CI 30.0-34.4). A total of 3678 patients achieved PFS24; SMR after achieving PFS24 was 1.22 (95% CI 1.09-1.37). The observed OS versus expected OS at 3, 5, and 7 years after achieving PFS24 was 93.1% versus 94.4%, 87.6% versus 89.5%, and 80.0% versus 83.7%, respectively.
Conclusion: Patients treated with rituximab containing anthracycline-based immunochemotherapy on clinical trials who are alive without progression at 24 months from the onset of initial therapy have excellent outcomes with survival that is marginally lower but clinically indistinguishable from the age-, sex-, and country-matched background population for 7 years after achieving PFS24.
Figures
Comment in
-
Surrogate end points in lymphoma.Ann Oncol. 2018 Aug 1;29(8):1622-1623. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy219. Ann Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29905757 No abstract available.
-
Progression-free survival at 24 months (PFS24) and subsequent outcome for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in the real-world setting.Ann Oncol. 2019 Jan 1;30(1):151-152. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy482. Ann Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30364941 No abstract available.
-
Reply to the letter to the editor 'Progression-free survival at 24 months (PFS24) and subsequent outcome for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in the real-world setting' by van der Galiën et al.Ann Oncol. 2019 Jan 1;30(1):153. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy492. Ann Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30395156 No abstract available.
References
-
- Al-Hamadani M, Habermann TM, Cerhan JR. et al. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtype distribution, geodemographic patterns, and survival in the US: a longitudinal analysis of the National Cancer Data Base from 1998 to 2011. Am J Hematol 2015; 90(9): 790–795. - PubMed
-
- Sant M, Allemani C, Tereanu C. et al. Incidence of hematologic malignancies in Europe by morphologic subtype: results of the HAEMACARE project. Blood 2010; 116(19): 3724–3734. - PubMed
-
- Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J. et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2002; 346(4): 235–242. - PubMed
-
- Pfreundschuh M, Trümper L, Österborg A. et al. CHOP-like chemotherapy plus rituximab versus CHOP-like chemotherapy alone in young patients with good-prognosis diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma: a randomised controlled trial by the MabThera International Trial (MInT) Group. Lancet Oncol 2006; 7(5): 379–391. - PubMed
-
- Habermann TM, Weller EA, Morrison VA. et al. Rituximab-CHOP versus CHOP alone or with maintenance rituximab in older patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24(19): 3121–3127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

