The structure of the RbBP5 β-propeller domain reveals a surface with potential nucleic acid binding sites
- PMID: 29897600
- PMCID: PMC6283417
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky199
The structure of the RbBP5 β-propeller domain reveals a surface with potential nucleic acid binding sites
Abstract
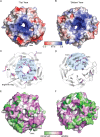
The multi-protein complex WRAD, formed by WDR5, RbBP5, Ash2L and Dpy30, binds to the MLL SET domain to stabilize the catalytically active conformation required for histone H3K4 methylation. In addition, the WRAD complex contributes to the targeting of the activated complex to specific sites on chromatin. RbBP5 is central to MLL catalytic activation, by making critical contacts with the other members of the complex. Interestingly its only major structural domain, a canonical WD40 repeat β-propeller, is not implicated in this function. Here, we present the structure of the RbBP5 β-propeller domain revealing a distinct, feature rich surface, dominated by clusters of Arginine residues. Our nuclear magnetic resonance binding data supports the hypothesis that in addition to the role of RbBP5 in catalytic activation, its β-propeller domain is a platform for the recruitment of the MLL complexes to chromatin targets through its direct interaction with nucleic acids.
Figures


References
-
- Berger S.L. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature. 2007; 447:407–412. - PubMed
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007; 128:693–705. - PubMed
-
- Schuettengruber B., Chourrout D., Vervoort M., Leblanc B., Cavalli G.. Genome regulation by polycomb and trithorax proteins. Cell. 2007; 128:735–745. - PubMed
-
- Ringrose L., Paro R.. Epigenetic regulation of cellular memory by the Polycomb and Trithorax group proteins. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2004; 38:413–443. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

