Intermolecular Metal-Catalyzed Reductive Coupling of Dienes, Allenes, and Enynes with Carbonyl Compounds and Imines
- PMID: 29897740
- PMCID: PMC6203947
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00213
Intermolecular Metal-Catalyzed Reductive Coupling of Dienes, Allenes, and Enynes with Carbonyl Compounds and Imines
Abstract
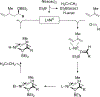
Metal-catalyzed reductive coupling has emerged as an alternative to the use of stoichiometric organometallic reagents in an increasingly diverse range of carbonyl and imine additions. In this review, the use of diene, allene, and enyne pronucleophiles in intermolecular carbonyl and imine reductive couplings are surveyed, along with related hydrogen autotransfer processes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
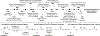

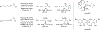
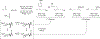
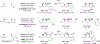
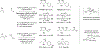
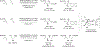
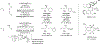
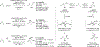
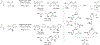
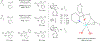


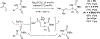
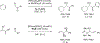
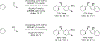
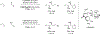
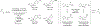
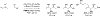
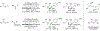
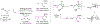

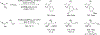


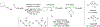
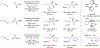
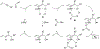
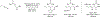


References
-
- Frankland E Isolation of Organic Radicals. Ann 1849, 71, 171–213.
-
- For a historical review, see: Seyferth D Zinc Alkyls, Edward Frankland, and the Beginnings of MainGroup Organometallic Chemistry. Organometallics 2001, 20, 2940–2955.
-
- For a historical review, see: Thayer JS Historical Origins of Organometallic Chemistry. J. Chem. Educ. 1969, 46, 764–765.
-
- Wanklyn JA Ueber die Bildung der Propionsäure aus Kohlensäure und eine Aethylverbindung. Ann. Chem. Pharm 1858, 107, 125–128.
-
- For a historical review, see: Seyferth D Alkyl and Aryl Derivatives of the Alkali Metals: Useful Synthetic Reagents as Strong Bases and Potent Nucleophiles. 1. Conversion of Organic Halides to Organoalkali-Metal Compounds. Organometallics 2006, 25, 2–24.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

