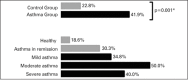
Levels of knowledge about asthma of parents of asthmatic children
- PMID: 29898088
- PMCID: PMC6063748
- DOI: 10.1590/S1679-45082018AO4204
Levels of knowledge about asthma of parents of asthmatic children
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the levels of knowledge about asthma of parents of school children.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was carried out with parents of children with medical diagnosis of asthma (mild, moderate and severe), followed up at an outpatient referral center for childhood asthma in the Southern region of Brazil (Asthma Group). Parents of children with asthma in remission and healthy children were also selected (Control Group). The Newcastle Asthma Knowledge Questionnaire (NAKQ) questionnaire was applied in both groups.
Results: A total of 154 parents of children participated in the study; in that, 62 (40.26%) in the Asthma Group, and 92 (59.74%) in the Control Group, with a mean age of 35.60±10.03 years. Of these, 132 (85.7%) were female, and 72 (46.8%) parents studied up to high school. The average score of level of knowledge was 18.06±4.11 points. Only 30.5% parents had acceptable levels of knowledge about asthma, which were more prevalent in the Asthma Group than in the Control Group (41.9% versus 22.8%, p=0.01). The mean score in Newcastle Asthma Knowledge Questionnaire (NAKQ) was higher in the Asthma Group (19.32±3.92 versus 17.21±4.03, p=0.001), respectively. The parents with mild and moderate asthmatic children scored more than those of severe asthma (19.5 and 19.9 versus 18.2 points, p=0.02).
Conclusion: Most parents had an unsatisfactory level of knowledge about asthma, which reinforces the need for changes in public asthma management programs.
Objetivo: Avaliar os níveis de conhecimento em asma de pais de crianças escolares.
Métodos: Foi realizado um estudo transversal, com pais de crianças com diagnóstico médico de asma (leve, moderada e grave), em acompanhamento ambulatorial em um centro de referência em asma infantil na Região Sul do Brasil (Grupo Asma). Foram também selecionados pais de crianças com asma em remissão e crianças saudáveis (Grupo Controle). Aplicou-se o questionário Newcastle Asthma Knowledge Questionnaire (NAKQ) em ambos os grupos.
Resultados: Participaram do estudo 154 pais de crianças, sendo 62 (40,26%) do Grupo Asma e 92 (59,74%) do Grupo Controle, com média de idade de 35,60±10,03 anos. Destes, 132 (85,7%) eram do sexo feminino e 72 (46,8%) eram pais com escolaridade até o Ensino Médio. A pontuação média do nível de conhecimento foi de 18,06±4,11 pontos. Apenas 30,5% dos pais apresentaram níveis aceitáveis de conhecimento em asma, os quais, por sua vez, foram mais prevalentes no Grupo Asma do que no Grupo Controle (41,9% versus 22,8%; p=0,01). E a média de pontuação no Newcastle Asthma Knowledge Questionnaire (NAKQ) foi maior no Grupo Asma (19,32±3,92 versus 17,21±4,03, p=0,001), respectivamente. Os pais de crianças com asma leve e moderada acertaram mais do que os de asma grave (19,5 e 19,9 versus 18,2 pontos; p=0,02).
Conclusão: A maioria dos pais apresentou nível insatisfatório de conhecimento sobre a asma, o que reforça a necessidade de mudanças nos programas públicos de manejo de asma.
Conflict of interest statement
none.
Figures
References
-
- Worldwide variation in prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and atopic eczema: ISAAC The International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) Steering Committee. Lancet. 1998;351(9111):1225–1232. - PubMed
-
- Roncada C, de Oliveira SG, Cidade SF, Sarria EE, Mattiello R, Ojeda BS, et al. Burden of asthma among inner-city children from Southern Brazil. J Asthma. 2016;53(5):498–504. - PubMed
-
- Boulet LP, FitzGerald JM, Reddel HK. The revised 2014 GINA strategy report: opportunities for change. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2015;21(1):1–7. Review. - PubMed
-
- Pitrez PM, Stein RT. Asthma in Latin America: the dawn of a new epidemic. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;8(5):378–383. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical