MicroRNA-644a promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by downregulating the expression of heat shock factor 1
- PMID: 29898735
- PMCID: PMC6001142
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-018-0244-z
MicroRNA-644a promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by downregulating the expression of heat shock factor 1
Erratum in
-
Correction: MicroRNA-644a promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by downregulating the expression of heat shock factor 1.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Sep 22;20(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00975-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 36138421 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
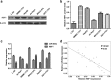
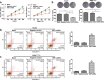
In this study, we investigated the role of microRNA-644a (miR-644a) in the growth and survival of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. MiR-644a levels were lower in HCC tissues than in adjacent peri-cancerous tissues (n = 135). MiR-644a expression was inversely correlated with heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) expression, tumour diameter and TNM stage. Moreover, HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cell lines showed lower miR-644a expression than normal L-O2 hepatocytes. MiR-644a overexpression in HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells increased apoptosis by downregulating HSF1. Dual luciferase reporter assays confirmed the presence of a miR-644a binding site in the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of HSF1. Xenograft tumours derived from SMMC-7721 cells transfected with a miR-664a mimic showed less growth than tumours derived from untransfected controls. Protein chip analysis revealed that miR-644a-overexpressing SMMC-7721 and HepG2 cells strongly expressed pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins, such as BID, BAD, BIM, SMAC, Apaf-1 and cleaved caspases-3 and -9. These findings suggest miR-644a promotes apoptosis in HCC cells by inhibiting HSF1.
Keywords: Apoptosis; BH3-only protein; HSF1; Hepatocellular carcinoma; miR-644a.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Clinical data have been approved by the Ethics Committee of Guilin Medical.
University and approved by the patients. All animal experiments were approved by Animal Care and Use Committee of Guilin Medical University.
Competing interests
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by all authors.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures







References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism. and function Cell. 2004;116(2):281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 81360367/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- No. 81560393/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 2016GXNSFFA380003/Guangxi Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars Program/International
- 2014GXNSFBA118192/Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province/International
- 2015jjDA40010/Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province/International
- Z2013466/Guangxi health department raise issue/International
- YB2014265/Fund project in Guangxi department of education/International
- GK2014-TKF01/Guangxi Regional High-risk Tumors Early Prevention and Control of Key Laboratory Open Research Project/International
- 20140310-2-2/Scientific Research and Technology Development Project for Guilin/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

