Directed evolution of a picomolar-affinity, high-specificity antibody targeting phosphorylated tau
- PMID: 29899114
- PMCID: PMC6078456
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003557
Directed evolution of a picomolar-affinity, high-specificity antibody targeting phosphorylated tau
Abstract
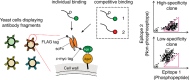
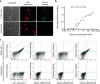
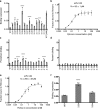
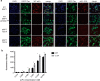
Antibodies are essential biochemical reagents for detecting protein post-translational modifications (PTMs) in complex samples. However, recent efforts in developing PTM-targeting antibodies have reported frequent nonspecific binding and limited affinity of such antibodies. To address these challenges, we investigated whether directed evolution could be applied to improve the affinity of a high-specificity antibody targeting phosphothreonine 231 (pThr-231) of the human microtubule-associated protein tau. On the basis of existing structural information, we hypothesized that improving antibody affinity may come at the cost of loss in specificity. To test this hypothesis, we developed a novel approach using yeast surface display to quantify the specificity of PTM-targeting antibodies. When we affinity-matured the single-chain variable antibody fragment through directed evolution, we found that its affinity can be improved >20-fold over that of the WT antibody, reaching a picomolar range. We also discovered that most of the high-affinity variants exhibit cross-reactivity toward the nonphosphorylated target site but not to the phosphorylation site with a scrambled sequence. However, systematic quantification of the specificity revealed that such a tradeoff between the affinity and specificity did not apply to all variants and led to the identification of a picomolar-affinity variant that has a matching high specificity of the original phosphotau antibody. In cell- and tissue-imaging experiments, the high-affinity variant gave significantly improved signal intensity while having no detectable nonspecific binding. These results demonstrate that directed evolution is a viable approach for obtaining high-affinity PTM-specific antibodies and highlight the importance of assessing the specificity in the antibody engineering process.
Keywords: affinity; anti-PTM antibody; antibody; antibody specificity; immunochemistry; neurodegeneration; phospho-specific; post-translational modification; protein phosphorylation; tau protein (tau).
© 2018 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
B. W. is cofounder and chief scientific officer of Aquinnah Pharmaceuticals Inc
Figures




Similar articles
-
Yeast biopanning against site-specific phosphorylations in tau.Protein Eng Des Sel. 2023 Jan 21;36:gzad005. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzad005. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2023. PMID: 37294629 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of novel affinity-matured human chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 antibody fragments by yeast display.Protein Eng Des Sel. 2017 Sep 1;30(9):639-647. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzx038. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2017. PMID: 28981720 Free PMC article.
-
Humanization of a phosphothreonine peptide-specific chicken antibody by combinatorial library optimization of the phosphoepitope-binding motif.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Jul 31;463(3):414-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.05.086. Epub 2015 May 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26036575
-
Beyond antibody engineering: directed evolution of alternative binding scaffolds and enzymes using yeast surface display.Microb Cell Fact. 2018 Feb 26;17(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12934-018-0881-3. Microb Cell Fact. 2018. PMID: 29482656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Directed evolution of proteins for increased stability and expression using yeast display.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012 Oct 15;526(2):174-80. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.04.022. Epub 2012 May 3. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22575387 Review.
Cited by
-
Derivation of splice junction-specific antibodies using a unique hapten targeting strategy and directed evolution.N Biotechnol. 2022 Nov 25;71:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2022.06.003. Epub 2022 Jun 22. N Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35750288 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery-stage identification of drug-like antibodies using emerging experimental and computational methods.MAbs. 2021 Jan-Dec;13(1):1895540. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2021.1895540. MAbs. 2021. PMID: 34313532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hierarchical sequence-affinity landscapes shape the evolution of breadth in an anti-influenza receptor binding site antibody.Elife. 2023 Jan 10;12:e83628. doi: 10.7554/eLife.83628. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36625542 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Phosphorylated-Tau Threonine 231 in Human Serum Using Interdigitated Wave-Shaped Electrode.Biomedicines. 2021 Dec 22;10(1):10. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010010. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 35052691 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast biopanning against site-specific phosphorylations in tau.Protein Eng Des Sel. 2023 Jan 21;36:gzad005. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzad005. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2023. PMID: 37294629 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

