Cryo-EM structure of human rhodopsin bound to an inhibitory G protein
- PMID: 29899450
- PMCID: PMC8054211
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0215-y
Cryo-EM structure of human rhodopsin bound to an inhibitory G protein
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Cryo-EM structure of human rhodopsin bound to an inhibitory G protein.Nature. 2018 Sep;561(7724):E44. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0302-0. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29930353
Abstract
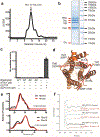
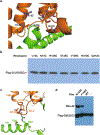
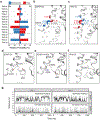
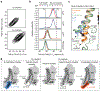
G-protein-coupled receptors comprise the largest family of mammalian transmembrane receptors. They mediate numerous cellular pathways by coupling with downstream signalling transducers, including the hetrotrimeric G proteins Gs (stimulatory) and Gi (inhibitory) and several arrestin proteins. The structural mechanisms that define how G-protein-coupled receptors selectively couple to a specific type of G protein or arrestin remain unknown. Here, using cryo-electron microscopy, we show that the major interactions between activated rhodopsin and Gi are mediated by the C-terminal helix of the Gi α-subunit, which is wedged into the cytoplasmic cavity of the transmembrane helix bundle and directly contacts the amino terminus of helix 8 of rhodopsin. Structural comparisons of inactive, Gi-bound and arrestin-bound forms of rhodopsin with inactive and Gs-bound forms of the β2-adrenergic receptor provide a foundation to understand the unique structural signatures that are associated with the recognition of Gs, Gi and arrestin by activated G-protein-coupled receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


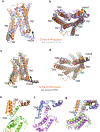


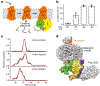
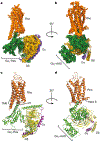

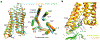
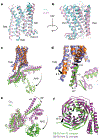
Comment in
-
How the ubiquitous GPCR receptor family selectively activates signalling pathways.Nature. 2018 Jun;558(7711):529-530. doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-05503-4. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29946098 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fredriksson R, Lagerström MC, Lundin LG & Schiöth HB The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol. Pharmacol 63, 1256–1272 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Neves SR, Ram PT & Iyengar R G protein pathways. Science 296, 1636–1639 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Zhou XE, Melcher K & Xu HE Understanding the GPCR biased signaling through G protein and arrestin complex structures. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 45, 150–159 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Palczewski K et al. Crystal structure of rhodopsin: a G protein-coupled receptor. Science 289, 739–745 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

