Targeted therapy in patients with PIK3CA-related overgrowth syndrome
- PMID: 29899452
- PMCID: PMC7610773
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0217-9
Targeted therapy in patients with PIK3CA-related overgrowth syndrome
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Targeted therapy in patients with PIK3CA-related overgrowth syndrome.Nature. 2019 Apr;568(7752):E6. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1109-3. Nature. 2019. PMID: 30944482
Abstract
CLOVES syndrome (congenital lipomatous overgrowth, vascular malformations, epidermal naevi, scoliosis/skeletal and spinal syndrome) is a genetic disorder that results from somatic, mosaic gain-of-function mutations of the PIK3CA gene, and belongs to the spectrum of PIK3CA-related overgrowth syndromes (PROS). This rare condition has no specific treatment and a poor survival rate. Here, we describe a postnatal mouse model of PROS/CLOVES that partially recapitulates the human disease, and demonstrate the efficacy of BYL719, an inhibitor of PIK3CA, in preventing and improving organ dysfunction. On the basis of these results, we used BYL719 to treat nineteen patients with PROS. The drug improved the disease symptoms in all patients. Previously intractable vascular tumours became smaller, congestive heart failure was improved, hemihypertrophy was reduced, and scoliosis was attenuated. The treatment was not associated with any substantial side effects. In conclusion, this study provides the first direct evidence supporting PIK3CA inhibition as a promising therapeutic strategy in patients with PROS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
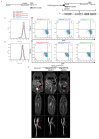

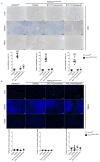
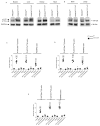
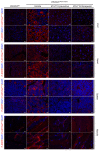
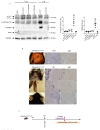

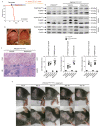


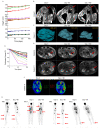
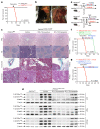
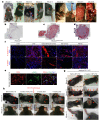
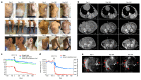
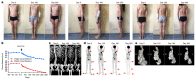

Comment in
-
Lessons for cancer drug treatment from tackling a non-cancerous overgrowth syndrome.Nature. 2018 Jun;558(7711):523-525. doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-05365-w. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29941899 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vanhaesebroeck B, Stephens L, Hawkins P. PI3K signalling: the path to discovery and understanding. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:195–203. - PubMed
-
- Hiles ID, et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: structure and expression of the 110 kd catalytic subunit. Cell. 1992;70:419–429. - PubMed
-
- Stephens L, et al. Protein kinase B kinases that mediate phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent activation of protein kinase B. Science. 1998;279:710–714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

