Surface expression of Cytokine Receptor-Like Factor 2 increases risk of relapse in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients harboring IKZF1 deletions
- PMID: 29899835
- PMCID: PMC5995260
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.25411
Surface expression of Cytokine Receptor-Like Factor 2 increases risk of relapse in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients harboring IKZF1 deletions
Abstract
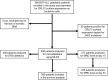
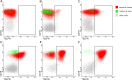
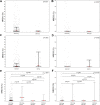
We prospectively examined whether surface expression of Cytokine Receptor-Like Factor 2 (CRLF2) on leukemic blasts is associated with survival and induction treatment response in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL) patients. Flow cytometric analysis of bone marrow-derived leukemia cells revealed that 7.51% (29/286) of 386 pediatric BCP-ALL patients were CRLF2-positive (CRLF2pos) at diagnosis. The median minimal residual disease (MRD) was lower in CRLF2pos than CRLF2-negative (CRLF2neg) patients on day 15 (MRD15) after induction therapy [0.01% (0.001-0.42%) vs. 0.45% (0.05-3.50%); p=0.001]. By contrast, the MRD15 was higher in Ikaros family Zinc Finger Protein 1 (IKZF1)-deleted BCP-ALL patients than in BCP-ALL patients without IKZF1 deletions [1.18% (0.06-12.0%) vs 0.33% (0.03-2.6%); p=0.003]. Subgroup analysis showed that MRD15 levels were lower in IKZF1Δ/CRLF2pos patients than in IKZF1Δ/CRLF2neg patients [0.1% (0.02-5.06%) vs. 2.9% (0.25-12%); p=0.005]. Furthermore, MRD15 levels were higher in IKZF1WT/CRLF2neg patients than in IKZF1WT/CRLF2pos patients [0.40% (0.04-2.7%) vs. 0.001% (0.001-0.01%)]. Despite the low MRD15 levels, IKZF1Δ/CRLF2pos patients showed poorer relapse-free survival (RFS) than other patient groups (p=0.003). These findings demonstrate that surface CRLF2 expression is associated with increased risk of relapse in pediatric BCP-ALL patients harboring IKZF1 deletions.
Keywords: acute lymphoblastic leukemia; gene; minimal residual disease; relapse.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Roberts KG. The biology of Philadelphia chromosome-like ALL. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2017;30:212–221. - PubMed
-
- Tallen G, Ratei R, Mann G, Kaspers G, Niggli F, Karachunsky A, Ebell W, Escherich G, Schrappe M, Klingebiel T, Fengler R, Henze G, von Stackelberg A. Long-term outcome in children with relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia after time-point and site-of-relapse stratification and intensified short-course multidrug chemotherapy: results of trial all-REZ BFM 90. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2339–2347. - PubMed
-
- Eckert C, von Stackelberg A, Seeger K, Groeneveld TW, Peters C, Klingebiel T, Borkhardt A, Schrappe M, Escherich G, Henze G. Minimal residual disease after induction is the strongest predictor of prognosis in intermediate risk relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia - long-term results of trial ALL-REZ BFM P95/96. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49:1346–55. - PubMed
-
- Roy A, Cargill A, Love S, Moorman AV, Stoneham S, Lim A, Darbyshire PJ, Lancaster D, Hann I, Eden T, Saha V. Outcome after first relapse in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia - lessons from the United Kingdom R2 trial. Br J Haematol. 2005;130:67–75. - PubMed
-
- Oskarsson T, Söderhäll S, Arvidson J, Forestier E, Montgomery S, Bottai M, Lausen B, Carlsen N, Hellebostad M, Lähteenmäki P, Saarinen-Pihkala UM, Jónsson ÓG, Heyman M. Relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the Nordic countries: prognostic factors, treatment and outcome. Haematologica. 2016;101:68–76. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

