Allograft and patient survival after sequential HSCT and kidney transplantation from the same donor-A multicenter analysis
- PMID: 29900661
- PMCID: PMC6585795
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.14970
Allograft and patient survival after sequential HSCT and kidney transplantation from the same donor-A multicenter analysis
Abstract
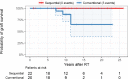
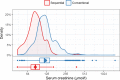
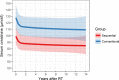
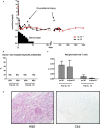
Tolerance induction through simultaneous hematopoietic stem cell and renal transplantation has shown promising results, but it is hampered by the toxicity of preconditioning therapies and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Moreover, renal function has never been compared to conventionally transplanted patients, thus, whether donor-specific tolerance results in improved outcomes remains unanswered. We collected follow-up data of published cases of renal transplantations after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from the same donor and compared patient and transplant kidney survival as well as function with caliper-matched living-donor renal transplantations from the Austrian dialysis and transplant registry. Overall, 22 tolerant and 20 control patients were included (median observation period 10 years [range 11 months to 26 years]). In the tolerant group, no renal allograft loss was reported, whereas 3 were lost in the control group. Median creatinine levels were 85 μmol/l (interquartile range [IQR] 72-99) in the tolerant cohort and 118 μmol/l (IQR 99-143) in the control group. Mixed linear-model showed around 29% lower average creatinine levels throughout follow-up in the tolerant group (P < .01). Our data clearly show stable renal graft function without long-term immunosuppression for many years, suggesting permanent donor-specific tolerance. Thus sequential transplantation might be an alternative approach for future studies targeting tolerance induction in renal allograft recipients.
Keywords: bone marrow/hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; clinical research/practice; kidney (allograft) function/dysfunction; kidney transplantation/nephrology; tolerance: clinical.
© 2018 The Authors American Journal of Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures

References
-
- Lamb KE, Lodhi S, Meier‐Kriesche HU. Long‐term renal allograft survival in the United States: a critical reappraisal. Am J Transplant. 2011;11(3):450‐462. - PubMed
-
- Pilat N, Wekerle T. Transplantation tolerance through mixed chimerism. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010;6(10):594‐605. - PubMed
-
- Billingham RE, Brent L, Medawar PB. Actively acquired tolerance of foreign cells. Nature. 1953;172(4379):603‐606. - PubMed
-
- Sayegh MH, Fine NA, Smith JL, Rennke HG, Milford EL, Tilney NL. Immunologic tolerance to renal allografts after bone marrow transplants from the same donors. Ann Intern Med. 1991;114(11):954‐955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

