CDMP1 overexpression mediates inflammatory cytokine‑induced apoptosis via inhibiting the Wnt/β‑Catenin pathway in rat dorsal root ganglia neurons
- PMID: 29901085
- PMCID: PMC6089779
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3716
CDMP1 overexpression mediates inflammatory cytokine‑induced apoptosis via inhibiting the Wnt/β‑Catenin pathway in rat dorsal root ganglia neurons
Abstract
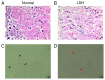
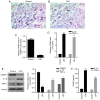
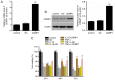
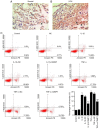
Cartilage‑derived morphogenetic protein‑1 (CDMP1) is a polypeptide growth factor with specific cartilage inducibility, which is predominantly expressed in the developmental long bone cartilage core and in the pre‑cartilage matrix in the embryonic stage. The aim of the present study was to investigate the roles and the mechanisms of CDMP1 overexpression on the apoptosis of rat dorsal root ganglia (DRG) neurons that were induced by inflammatory cytokines. Cell counting Kit‑8 assay, flow cytometry and TdT‑mediated dUTP nick‑end labeling assay were performed to examine cell viability and apoptosis. ELISA, hematoxylin and eosin staining and immunohistochemistry assays were performed to examine the levels of several factors in DRG tissues. Western blot analysis and reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction assays were used to determine the mRNA and protein expression levels, respectively. The results demonstrated that CDMP1 expression was downregulated, while inflammatory cytokine expression was upregulated in DRG tissues derived from lumbar disc herniation (LDH) model rats. In addition, DRG cells from LDH rats exhibited increased apoptosis compared with control rats. CDMP1 overexpression enhanced the cell viability of inflammatory cytokine‑induced DRG cells, and suppressed the apoptosis of inflammatory cytokine‑induced DRG cells via regulating the expression levels of Caspase‑3/8/9, BCL2 apoptosis regulator, and BCL2 associated X. Furthermore, CDMP1 overexpression was demonstrated to affect the Wnt/β‑Catenin pathway in the inflammatory cytokine‑induced DRG cells. In conclusion, the present findings suggested that CDMP1 overexpression mediated inflammatory cytokine‑induced apoptosis via Wnt/β‑Catenin signaling in rat DRG cells.
Figures
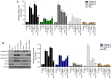
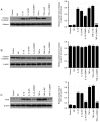
References
-
- Raghavendra V, Tanga F, Rutkowski MD, DeLeo JA. Anti-hyperalgesic and morphine-sparing actions of propentofylline following peripheral nerve injury in rats: Mechanistic implications of spinal glia and proinflammatory cytokines. Pain. 2003;104:655–664. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3959(03)00138-6. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

