Telomerase reverse transcriptase induced thyroid carcinoma cell proliferation through PTEN/AKT signaling pathway
- PMID: 29901196
- PMCID: PMC6072153
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9119
Telomerase reverse transcriptase induced thyroid carcinoma cell proliferation through PTEN/AKT signaling pathway
Abstract
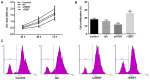
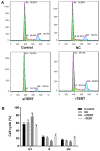
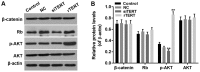
Thyroid carcinoma is the most common endocrine malignant tumor in the world, and so, there is a requirement to develop novel molecular targets for thyroid cancer diagnosis and treatment. Telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) was revealed to promote cell proliferation in a number of types of cell. To evaluate whether and how TERT functioned on papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) cell proliferation, the present study constructed TERT over‑expression [recombined (r)TERT plasmid group] and interference [small interfering RNA (si)‑TERT group] models by liposome transfection respectively to study the molecular mechanisms. The transfection efficiency was first detected by reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT‑qPCR) and western blotting to analyze TERT levels compared with the negative control (NC) and control groups. Then MTT and carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester assays were performed to determine living cell proliferation and total cell proliferation respectively. Propidium iodide assay was used to detect alterations in cell cycle progression. RT‑qPCR and western blotting were performed to detect associated factor variation. The results demonstrated that, following the generation of TERT overexpression or silencing PTC cells, the living cells and also total cell proliferation increased significantly in the rTERT group, and decreased significantly in siTERT group, when compared with the NC and control groups. The cell cycle was accelerated in the rTERT group, and blocked in the G1/S transition in the siTERT group. The mRNA and protein levels of P27, P53 and phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) decreased significantly in the rTERP group and increased in the siTERP group, while cyclin dependent kinase 2 and Cyclin D1 increased significantly in the rTERP group and decreased in the siTERP group. The expression of cell division cycle 25A did not alter significantly. The protein levels of β‑catenin and retinoblastoma were also unaltered. Protein kinase B (AKT) was detected once activated by TERT, and there were increased phosphorylated (p)‑AKT protein levels in the rTERT group, and decreased p‑AKT protein levels in the siTERT group. In conclusion, TERT could induce thyroid carcinoma cell proliferation mainly through the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway.
Figures
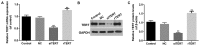

References
-
- Albores-Saavedra J, Henson DE, Glazer E, Schwartz AM. Changing patterns in the incidence and survival of thyroid cancer with follicular phenotype-papillary, follicular, and anaplastic: A morphological and epidemiological study. Endocr Pathol. 2007;18:1–7. doi: 10.1007/s12022-007-0002-z. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

