Use of a Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Following a Fracture-Dislocation with a Brachial Plexus Palsy: A Case Report
- PMID: 29901477
- PMCID: PMC6427917
- DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.CC.17.00204
Use of a Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Following a Fracture-Dislocation with a Brachial Plexus Palsy: A Case Report
Abstract
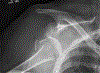
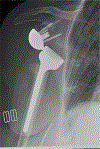
Case: An 80-year-old woman sustained a fracture-dislocation of the proximal aspect of the humerus with a near-complete brachial plexopathy, which was successfully managed acutely using a reverse shoulder arthroplasty (RSA) with repair of the greater and lesser tuberosities. The palsy, which was confirmed with nerve conduction studies, recovered uneventfully along with functional improvement of the shoulder. At the most recent follow-up, there was complete resolution of the plexopathy, with excellent, pain-free range of motion.
Conclusion: Acute RSA with tuberosity repair may be a reasonable treatment modality in the setting of an acute brachial plexus palsy following a comminuted fracture-dislocation of the proximal aspect of the humerus in an elderly patient.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
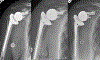
References
-
- McLaughlin JA, Light R, Lustrin I. Axillary artery injury as a complication of proximal humerus fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998. May-Jun;7(3):292–4. - PubMed
-
- Launonen AP, Lepola V, Saranko A, Flinkkilä T, Laitinen M, Mattila VM. Epidemiology of proximal humerus fractures. Arch Osteoporos. 2015;10:209 Epub 2015 Feb 13. - PubMed
-
- Visser CP, Tavy DL, Coene LN, Brand R. Electromyographic findings in shoulder dislocations and fractures of the proximal humerus: comparison with clinical neurological examination. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1999. June;101(2):86–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

