Pharmacokinetics of Co-Suspension Delivery Technology Budesonide/Glycopyrronium/Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate (BGF MDI) and Budesonide/Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate (BFF MDI) Fixed-Dose Combinations Compared With an Active Control: A Phase 1, Randomized, Single-Dose, Crossover Study in Healthy Adults
- PMID: 29901860
- PMCID: PMC6585691
- DOI: 10.1002/cpdd.585
Pharmacokinetics of Co-Suspension Delivery Technology Budesonide/Glycopyrronium/Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate (BGF MDI) and Budesonide/Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate (BFF MDI) Fixed-Dose Combinations Compared With an Active Control: A Phase 1, Randomized, Single-Dose, Crossover Study in Healthy Adults
Abstract
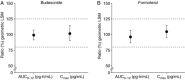
This randomized, phase 1, single-dose, crossover study (NCT02189304) compared the 12-hour pharmacokinetic (PK) and safety profiles of budesonide/glycopyrronium/formoterol fumarate dihydrate metered dose inhaler (BGF MDI) 320/14.4/10 μg and budesonide/formoterol fumarate dihydrate (BFF) MDI 320/10 μg (both formulated using innovative co-suspension delivery technology) to an active comparator (budesonide/formoterol fumarate dihydrate dry powder inhaler [BUD/FORM DPI] 320/9-μg delivered dose) in healthy adults. The potential for PK interaction between glycopyrronium and budesonide/formoterol within BGF MDI was assessed. Of 72 subjects randomized, 59 completed treatment. Systemic budesonide exposure (primary objective) based on area under the plasma drug concentration-time curve 0-12 hours (AUC0-12 ; % coefficient of variation) was 1598.38 (49.7), 1657.09 (50.4), and 1276.75 (70.4) pg·h/mL for BGF MDI, BFF MDI, and BUD/FORM DPI, respectively; and formoterol exposure (AUC0-12 [% coefficient of variation]) was 39.16 (45.9), 39.53 (40.5), and 23.24 (59.2) pg·h/mL, respectively. BGF MDI and BFF MDI were bioequivalent for budesonide and formoterol. All treatments were well tolerated. While systemic exposure to budesonide and formoterol was higher for BGF MDI and BFF MDI than for BUD/FORM DPI, there were no appreciable differences in the incidence of pharmacologically predictable adverse events. This, coupled with the absence of PK interactions, suggests the BGF MDI safety profile will be comparable to BUD/FORM DPI.
Keywords: COPD; co-suspension delivery technology; fixed-dose combination; metered dose inhaler; pharmacokinetics.
© 2018 The Authors. Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The pharmacokinetics of three doses of budesonide/glycopyrronium/formoterol fumarate dihydrate metered dose inhaler compared with active controls: A Phase I randomized, single-dose, crossover study in healthy adults.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Jun;50:11-18. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29544728 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics of budesonide/glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate metered dose inhaler formulated using co-suspension delivery technology after single and chronic dosing in patients with COPD.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Feb;60:101873. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2019.101873. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31841699 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics and Tolerability of Budesonide/Glycopyrronium/Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate and Glycopyrronium/Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate Metered Dose Inhalers in Healthy Chinese Adults: A Randomized, Double-blind, Parallel-group Study.Clin Ther. 2019 May;41(5):897-909.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.03.007. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Clin Ther. 2019. PMID: 30982547 Clinical Trial.
-
Budesonide/Glycopyrrolate/Formoterol Fumarate Co-suspension Metered Dose Inhaler: A Triple Therapy for the Treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Ann Pharmacother. 2022 May;56(5):582-591. doi: 10.1177/10600280211038353. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Ann Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 34382422 Review.
-
Consistent Pulmonary Drug Delivery with Whole Lung Deposition Using the Aerosphere Inhaler: A Review of the Evidence.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021 Jan 18;16:113-124. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S274846. eCollection 2021. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021. PMID: 33500616 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Efficacy and Safety of Budesonide/Glycopyrronium/Formoterol in the Treatment of COPD in the Elderly.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Aug 17;2022:8382295. doi: 10.1155/2022/8382295. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. Retraction in: Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9819710. doi: 10.1155/2023/9819710. PMID: 36072633 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Effect of inhaled budesonide/formoterol fumarate dihydrate delivered via two different devices on lung function in patients with COPD and low peak inspiratory flow.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2022 Jan-Dec;16:17534666221107312. doi: 10.1177/17534666221107312. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2022. PMID: 35815354 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
International expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer complicated by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023 Aug 30;12(8):1661-1701. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-23-339. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37691866 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- European Respiratory Society . European Lung White Book. 2013. http://www.erswhitebook.org/. Accessed December 14, 2017.
-
- World Health Organization . Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Fact sheet. 2017. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs315/en/. Accessed June 13, 2017.
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease . Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD. 2018. http://www.goldcopd.org. Accessed November 15, 2017.
-
- Calverley P, Vlies B. A rational approach to single, dual and triple therapy in COPD. Respirology. 2016;21(4):581–589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

