Geographical variation of overweight, obesity and related risk factors: Findings from the European Health Examination Survey in Luxembourg, 2013-2015
- PMID: 29902172
- PMCID: PMC6001977
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197021
Geographical variation of overweight, obesity and related risk factors: Findings from the European Health Examination Survey in Luxembourg, 2013-2015
Abstract
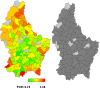
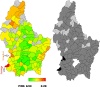
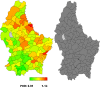
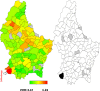
The analyses of geographic variations in the prevalence of major chronic conditions, such as overweight and obesity, are an important public health tool to identify "hot spots" and inform allocation of funding for policy and health promotion campaigns, yet rarely performed. Here we aimed at exploring, for the first time in Luxembourg, potential geographic patterns in overweight/obesity prevalence in the country, adjusted for several demographic, socioeconomic, behavioural and health status characteristics. Data came from 720 men and 764 women, 25-64 years old, who participated in the European Health Examination Survey in Luxembourg (2013-2015). To investigate the geographical variation, geo-additive semi-parametric mixed model and Bayesian modelisations based on Markov Chain Monte Carlo techniques for inference were performed. Large disparities in the prevalence of overweight and obesity were found between municipalities, with the highest rates of obesity found in 3 municipalities located in the South-West of the country. Bayesian approach also underlined a nonlinear effect of age on overweight and obesity in both genders (significant in men) and highlighted the following risk factors: 1. country of birth for overweight in men born in a non-European country (Posterior Odds Ratio (POR): 3.24 [1.61-8.69]) and women born in Portugal (POR: 2.44 [1.25-4.43]), 2. low educational level (secondary or below) for overweight (POR: 1.66 (1.06-2.72)] and obesity (POR:2.09 [1.05-3.65]) in men, 3. single marital status for obesity in women (POR: 2.20 [1.24-3.91]), 4.fair (men: POR: 3.19 [1.58-6.79], women: POR: 2.24 [1.33-3.73]) to very bad health perception (men: POR: 15.01 [2.16-98.09]) for obesity, 5. sleeping more than 6 hours for obesity in unemployed men (POR: 3.66 [2.02-8.03]). Protective factors highlighted were: 1. single marital status against overweight (POR: [0.60 (0.38-0.96)]) and obesity (POR: 0.39 [0.16-0.84]) in men, 2. the fact to be widowed against overweight in women (POR: [0.30 (0.07-0.86)], as well as a non European country of birth (POR: 0.49 [0.19-0.98]), tertiary level of education (POR: 0.34 [0.18-0.64]), moderate alcohol consumption (POR: 0.54 [0.36-0.90]) and aerobic physical activity practice (POR: 0.44 [0.27-0.77]) against obesity in women. A double burden of environmental exposure due to historic mining and industrial activities and past economic vulnaribility in the South-West of the country may have participated to the higher prevalence of obesity found in this region. Other demographic, socioeconomic, behavioural and health status covariates could have been involved as well.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384(9945):766–81. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Worldometers. Population mondiale actuelle 2016 [13th June 2016]. Available from: http://www.worldometers.info/fr/population-mondiale/.
-
- G. B. D. Risk Factors Collaborators, Forouzanfar MH, Alexander L, Anderson HR, Bachman VF, Biryukov S, et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00128-2 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Conscienhealth. 57 Varieties of Obesity: Moving Past One Size Fits All. Adapted from Kaplan L., presentation at the 29th Blackburn Course in Obesity Medicine, June 2, 2016. [16th June 2016]. Available from: http://conscienhealth.org/2016/06/57-varieties-obesity-moving-past-one-s....
-
- The Obesity Society Infographic Task Force. Potential Contributors to Obesity 2015 [15th June 2016]. Available from: http://www.obesity.org/obesity/resources/facts-about-obesity/infographic....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

