A potential therapeutic role for angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in human pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 29903860
- PMCID: PMC6613216
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.02638-2017
A potential therapeutic role for angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in human pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
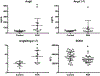
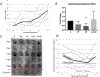
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a deadly disease with no cure. Alternate conversion of angiotensin II (AngII) to angiotensin-(1-7) (Ang-(1-7)) by angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) resulting in Mas receptor (Mas1) activation improves rodent models of PAH. Effects of recombinant human (rh) ACE2 in human PAH are unknown. Our objective was to determine the effects of rhACE2 in PAH.We defined the molecular effects of Mas1 activation using porcine pulmonary arteries, measured AngII/Ang-(1-7) levels in human PAH and conducted a phase IIa, open-label pilot study of a single infusion of rhACE2 (GSK2586881, 0.2 or 0.4 mg·kg-1 intravenously).Superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) and inflammatory gene expression were identified as markers of Mas1 activation. After confirming reduced plasma ACE2 activity in human PAH, five patients were enrolled in the trial. GSK2586881 was well tolerated with significant improvement in cardiac output and pulmonary vascular resistance. GSK2586881 infusion was associated with reduced plasma markers of inflammation within 2-4 h and increased SOD2 plasma protein at 2 weeks.PAH is characterised by reduced ACE2 activity. Augmentation of ACE2 in a pilot study was well tolerated, associated with improved pulmonary haemodynamics and reduced markers of oxidant and inflammatory mediators. Targeting this pathway may be beneficial in human PAH.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01884051.
Copyright ©ERS 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: A.R. Hemnes reports grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Cardiovascular Medical Research and Education Fund, personal fees from Actelion, Bayer and United Therapeutics, and personal fees and nonfinancial support (drug supplies to perform experiments) from GlaxoSmithKline, during the conduct of the study. In addition, she has a patent Annamometer issued (noninvasive diagnosis of pulmonary vascular disease). E.A. Austin has received grants from the NIH. He has served as a consultant to Acceleron. E.L. Brittain has received grants from the NIH. He has served as a consultant to Hovine Pharmaceuticals. E.J. Carrier has received grants from the NIH. She has intellectual property pending with Cumberland Pharmaceuticals and has received a grant from this entity. J.P. Fessel has received grant support from the NIH, Gilead, Actelion, the LAM foundation and the Parker B. Francis Foundation. C.D. Fike is a co-inventor on patent applications filed on behalf of Vanderbilt University in the USA and abroad and licensed to Asklepion Pharmaceuticals for the use of intravenous citrulline in lung conditions, without current financial compensation. J.H. Newman has received grants from the NIH. M.E. Pugh has received grant funding from the NIH and has served as a consultant to Gilead. T.W. Rice has received grant funding from the NIH. He has served as a consultant to Avisa Pharma, ACI Clinical and Nestle. He is the Director of Medical Affairs at Cumberland Pharmaceuticals. I.M. Robbins has received funding from the NIH. J.E. Loyd has received grants from the NIH. J. West has received grants from the NIH and Cumberland Pharmaceuticals, and holds intellectual property without financial gain at Cumberland Pharmaceuticals.
Figures



References
-
- de Man FS, Tu L, Handoko ML, Rain S, Ruiter G, Francois C, Schalij I, Dorfmuller P, Simonneau G, Fadel E, Perros F, Boonstra A, Postmus PE, van der Velden J, Vonk-Noordegraaf A, Humbert M, Eddahibi S and Guignabert C. Dysregulated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system contributes to pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186:780–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morrell NW, Danilov SM, Satyan KB, Morris KG and Stenmark KR. Right ventricular angiotensin converting enzyme activity and expression is increased during hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Cardiovasc Res. 1997;34:393–403. - PubMed
-
- Morrell NW, Morris KG and Stenmark KR. Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme and angiotensin II in development of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:H1186–94. - PubMed
-
- Alpert MA, Pressly TA, Mukerji V, Lambert CR and Mukerji B. Short- and long-term hemodynamic effects of captopril in patients with pulmonary hypertension and selected connective tissue disease. Chest. 1992;102:1407–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
