Real-time Genomic Characterization of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer to Enable Precision Medicine
- PMID: 29903880
- PMCID: PMC6192263
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0275
Real-time Genomic Characterization of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer to Enable Precision Medicine
Abstract
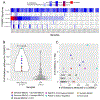
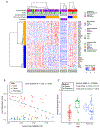
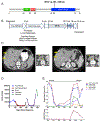
Clinically relevant subtypes exist for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), but molecular characterization is not yet standard in clinical care. We implemented a biopsy protocol to perform time-sensitive whole-exome sequencing and RNA sequencing for patients with advanced PDAC. Therapeutically relevant genomic alterations were identified in 48% (34/71) and pathogenic/likely pathogenic germline alterations in 18% (13/71) of patients. Overall, 30% (21/71) of enrolled patients experienced a change in clinical management as a result of genomic data. Twenty-six patients had germline and/or somatic alterations in DNA-damage repair genes, and 5 additional patients had mutational signatures of homologous recombination deficiency but no identified causal genomic alteration. Two patients had oncogenic in-frame BRAF deletions, and we report the first clinical evidence that this alteration confers sensitivity to MAPK pathway inhibition. Moreover, we identified tumor/stroma gene expression signatures with clinical relevance. Collectively, these data demonstrate the feasibility and value of real-time genomic characterization of advanced PDAC.Significance: Molecular analyses of metastatic PDAC tumors are challenging due to the heterogeneous cellular composition of biopsy specimens and rapid progression of the disease. Using an integrated multidisciplinary biopsy program, we demonstrate that real-time genomic characterization of advanced PDAC can identify clinically relevant alterations that inform management of this difficult disease. Cancer Discov; 8(9); 1096-111. ©2018 AACR.See related commentary by Collisson, p. 1062This article is highlighted in the In This Issue feature, p. 1047.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosure: Matthew B. Yurgelun acknowledges research funding from Myriad Genetic Laboratories, Inc. James M. Cleary reports research funding from Merck. Geoffrey I. Shapiro reports research funding from Lilly, Merck, EMD Serono, Sierra Oncology and Pfizer and is a consultant to Pfizer, G1 Therapeutics, Lilly, Roche and Merck/EMD Serono. Charles S. Fuchs is a consultant to CytomX, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, Merck and Entrinsic Health. Levi A. Garraway is an employee of Eli Lilly and Company and has ownership interest in Tango Therapeutic and Foundation Medicine. Bruce E. Johnson reports research funding from Toshiba and Novartis. Nikhil Wagle reports ownership interest in Foundation Medicine. Ryan B. Corcoran reports research funding from AstraZeneca and Sanofi, and is a consultant to Astex, Amgen, Avidity Biosciences, BMS, FOG Pharma, Genentech, LOXO Oncology, Merrimack, N-of-one, Roche, Roivant, Shire, Symphogen, Taiho and WarpDrive Bio. Richard B. Lanham is an employee of and has ownership interest in Guardant Health, Inc. Dean J. Welsch is an employee of BioMed Valley Discoveries. Brian M. Wolpin acknowledges research funding from Celgene. The remaining authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Bringing Pancreas Cancer into the Lab.Cancer Discov. 2018 Sep;8(9):1062-1063. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0811. Cancer Discov. 2018. PMID: 30181169
References
-
- Roberts NJ, Norris AL, Petersen GM, Bondy ML, Brand R, Gallinger S, et al. Whole Genome Sequencing Defines the Genetic Heterogeneity of Familial Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer discovery 2016;6(2):166–75 doi 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0402. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

