Soluble Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor in Black Americans with CKD
- PMID: 29903900
- PMCID: PMC6032570
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.13631217
Soluble Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor in Black Americans with CKD
Abstract
Background and objectives: Black Americans with and without APOL1 kidney disease risk variants face high risk of ESKD. Soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR), a circulating signaling protein and marker of immune activation, constitutes a promising biomarker of CKD-associated risks. We aimed to quantify the associations between serum suPAR concentration and adverse outcomes in Black Americans with and without APOL1 kidney disease risk variants, over and above iodine-125 iothalamate measured GFR and proteinuria.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Using data from the African-American Study of Kidney Disease and Hypertension, a multicenter clinical trial followed by a cohort phase with a median total follow-up of 9.7 years (interquartile range, 6.5-10.9 years), we examined the associations of suPAR with CKD progression (defined as doubling of serum creatinine or ESKD), ESKD, worsening proteinuria (defined as pre-ESKD doubling of 24-hour urine protein-to-creatinine ratio to ≥220 mg/g), and all-cause death.
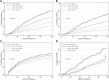
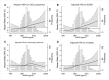
Results: At baseline, the median suPAR was 4462 pg/ml, mean measured GFR was 46 ml/min per 1.73 m2, and median 24-hour urine protein-to-creatinine ratio was 80 mg/g. After controlling for baseline demographics, randomization arm, GFR, proteinuria, APOL1 risk status, and clinical risk factors, there was a 1.26-times higher risk for CKD progression per SD higher baseline log-transformed suPAR (hazard ratio [HR], 1.26; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 1.11 to 1.43; P<0.001). Higher suPAR was also independently associated with risk of ESKD (HR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.17 to 1.58; P<0.001) and death (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.08 to 1.45; P=0.003). suPAR was only associated with worsening proteinuria in patients with two APOLI risk alleles (HR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.08 to 1.99; P=0.02).
Conclusions: Higher suPAR was associated with various adverse outcomes in Black Americans with CKD, with and without APOL1 kidney disease risk variants, independently of proteinuria and GFR.
Keywords: African Americans; Alleles; Biomarkers; Black Americans; Demography; Follow-Up Studies; Humans; Iothalamic Acid; Kidney Failure, Chronic; Random Allocation; Receptors, Urokinase Plasminogen Activator; Renal Insufficiency, Chronic; United States; chronic kidney disease; creatinine; glomerular filtration rate; hypertension; kidney; proteinuria; risk factors.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Thomas B, Matsushita K, Abate KH, Al-Aly Z, Ärnlöv J, Asayama K, Atkins R, Badawi A, Ballew SH, Banerjee A, Barregård L, Barrett-Connor E, Basu S, Bello AK, Bensenor I, Bergstrom J, Bikbov B, Blosser C, Brenner H, Carrero JJ, Chadban S, Cirillo M, Cortinovis M, Courville K, Dandona L, Dandona R, Estep K, Fernandes J, Fischer F, Fox C, Gansevoort RT, Gona PN, Gutierrez OM, Hamidi S, Hanson SW, Himmelfarb J, Jassal SK, Jee SH, Jha V, Jimenez-Corona A, Jonas JB, Kengne AP, Khader Y, Khang YH, Kim YJ, Klein B, Klein R, Kokubo Y, Kolte D, Lee K, Levey AS, Li Y, Lotufo P, El Razek HMA, Mendoza W, Metoki H, Mok Y, Muraki I, Muntner PM, Noda H, Ohkubo T, Ortiz A, Perico N, Polkinghorne K, Al-Radaddi R, Remuzzi G, Roth G, Rothenbacher D, Satoh M, Saum KU, Sawhney M, Schöttker B, Shankar A, Shlipak M, Silva DAS, Toyoshima H, Saum KU, Sawhney M, Schöttker B, Shankar A, Shlipak M, Silva DAS, Toyoshima H, Ukwaja K, Umesawa M, Vollset SE, Warnock DG, Werdecker A, Yamagishi K, Yano Y, Yonemoto N, Zaki MES, Naghavi M, Forouzanfar MH, Murray CJL, Coresh J, Vos T; Global Burden of Disease 2013 GFR Collaborators; CKD Prognosis Consortium; Global Burden of Disease Genitourinary Expert Group : Global cardiovascular and renal outcomes of reduced GFR. J Am Soc Nephrol 28: 2167–2179, 2017 - PMC - PubMed
-
- United States Renal Data System : USRDS 2010 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2016
-
- Wei C, El Hindi S, Li J, Fornoni A, Goes N, Sageshima J, Maiguel D, Karumanchi SA, Yap HK, Saleem M, Zhang Q, Nikolic B, Chaudhuri A, Daftarian P, Salido E, Torres A, Salifu M, Sarwal MM, Schaefer F, Morath C, Schwenger V, Zeier M, Gupta V, Roth D, Rastaldi MP, Burke G, Ruiz P, Reiser J: Circulating urokinase receptor as a cause of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Med 17: 952–960, 2011 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hahm E, Wei C, Fernandez I, Li J, Tardi NJ, Tracy M, Wadhwani S, Cao Y, Peev V, Zloza A, Lusciks J, Hayek SS, O’Connor C, Bitzer M, Gupta V, Sever S, Sykes DB, Scadden DT, Reiser J: Bone marrow-derived immature myeloid cells are a main source of circulating suPAR contributing to proteinuric kidney disease. Nat Med 23: 100–106, 2017 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

