Temporal and spectral EEG dynamics can be indicators of stealth placement
- PMID: 29904124
- PMCID: PMC6002479
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-27294-4
Temporal and spectral EEG dynamics can be indicators of stealth placement
Abstract
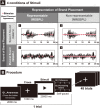
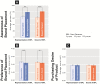
Stealth placement marketing, where consumers are unaware that they are being marketed to, attempts to reduce the audiences' resistance to traditional persuasive advertising. It is a form of advertising that involves targeted exposure of brands or products incorporated in other works, usually with or without explicit reference to the brands or products. Brand placement can be presented in different visual and auditory forms in video programs. The present study proposed that different 'representations' (i.e., representable or non-representable) and 'sounds' (i.e., speech or musical sound) of brand placement can affect the viewers' perception of the brand. Event-related potential results indicated significant differences in P1, N1, P2, N270, and P3. Further, event-related spectral perturbation results indicated significant differences in theta, alpha, beta, and gamma (30-100 Hz), in the right parietal, right occipital area, and limbic lobe. 'Non-representable' or 'speech sound' brand placement induced significant temporal and spectral EEG dynamics in viewers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Azevedo, P. C. B. S. d. Perception of commercial brands and the emotional and social value: A spatiotemporal EEG analysis. (2010).
-
- Ohme R, Reykowska D, Wiener D, Choromanska A. Analysis of neurophysiological reactions to advertising stimuli by means of EEG and galvanic skin response measures. Journal of Neuroscience, Psychology, and Economics. 2009;2:21. doi: 10.1037/a0015462. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

