The role of miR-122 in the dysregulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) expression in hepatocellular cancer
- PMID: 29904144
- PMCID: PMC6002539
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-27358-5
The role of miR-122 in the dysregulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) expression in hepatocellular cancer
Abstract
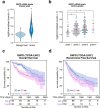
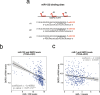
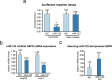
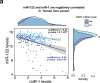
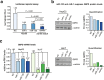
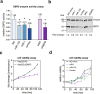
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Thus, a better understanding of molecular aberrations involved in HCC pathogenesis is necessary for developing effective therapy. It is well established that cancer cells metabolize energy sources differently to rapidly generate biomass. Glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (G6PD), the rate-limiting enzyme of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP), is often activated in human malignancies to generate precursors for nucleotide and lipid synthesis. Here, we determined the clinical significance of G6PD in primary human HCC by analyzing RNA-seq and clinical data in The Cancer Genome Atlas. We found that the upregulation of G6PD correlates with higher tumor grade, increased tumor recurrence, and poor patient survival. Notably, liver-specific miR-122, which is essential for metabolic homeostasis, suppresses G6PD expression by directly interacting with its 3'UTR. Luciferase reporter assay confirmed two conserved functional miR-122 binding sites located in the 3'-UTR of G6PD. Furthermore, we show that ectopic expression of miR-122 and miR-1, a known regulator of G6PD expression coordinately repress G6PD expression in HCC cells. These miRNAs also reduced G6PD activity in HepG2 cells that express relatively high activity of this enzyme. Collectively, this study provides evidence that anti-HCC efficacy of miR122 and miR-1 could be mediated, at least in part, through inhibition of PPP by suppressing the expression of G6PD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-450b-3p inhibits cell growth by targeting phosphoglycerate kinase 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Nov;120(11):18805-18815. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29196. Epub 2019 Jun 21. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31222833
-
miR-206-G6PD axis regulates lipogenesis and cell growth in hepatocellular carcinoma cell.Anticancer Drugs. 2021 Jun 1;32(5):508-516. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001069. Anticancer Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33735119
-
miR-206 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion, and migration by down-regulating PTP1B in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2019 May 15;39(5):BSR20181823. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181823. Print 2019 May 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31048362 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the circular RNA/microRNA/glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase axis in the pathological mechanism of hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2021 Dec;20(6):530-534. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2021.08.013. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2021. PMID: 34548225
-
The Emerging Roles of the Metabolic Regulator G6PD in Human Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 7;24(24):17238. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417238. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139067 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Multiple Roles of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase in Tumorigenesis and Cancer Chemoresistance.Life (Basel). 2022 Feb 12;12(2):271. doi: 10.3390/life12020271. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Targets and Signaling Pathways of microRNA-122 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 29;14(7):1380. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071380. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35890276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic reprogramming of glucose: the metabolic basis for the occurrence and development of hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 6;15:1545086. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1545086. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39980550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncovering Novel Roles of miR-122 in the Pathophysiology of the Liver: Potential Interaction with NRF1 and E2F4 Signaling.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 16;15(16):4129. doi: 10.3390/cancers15164129. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627157 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress in the metabolic reprogramming of hepatocellular carcinoma (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2024 Jul;30(1):131. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13255. Epub 2024 May 31. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38818815 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

