Phenotypic spectrum of Au-Kline syndrome: a report of six new cases and review of the literature
- PMID: 29904177
- PMCID: PMC6117294
- DOI: 10.1038/s41431-018-0187-2
Phenotypic spectrum of Au-Kline syndrome: a report of six new cases and review of the literature
Abstract
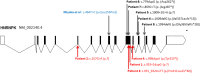
Au-Kline syndrome (AKS, OMIM 616580) is a multiple malformation syndrome, first reported in 2015, associated with intellectual disability. AKS has been associated with de novo loss-of-function variants in HNRNPK (heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein K), and to date, only four of these patients have been described in the literature. Recently, an additional patient with a missense variant in HNRNPK was also reported. These patients have striking facial dysmorphic features, including long palpebral fissures, ptosis, deeply grooved tongue, broad nose, and down-turned mouth. Patients frequently also have skeletal and connective tissue anomalies, craniosynostosis, congenital heart malformations, and renal anomalies. In this report, we describe six new patients and review the clinical information on all reported AKS patients, further delineating the phenotype of AKS. There are now a total of 9 patients with de novo loss-of-function variants in HNRNPK, one individual with a de novo missense variant in addition to 3 patients with de novo deletions of 9q21.32 that encompass HNRNPK. While there is considerable overlap between AKS and Kabuki syndrome (KS), these additional patients demonstrate that AKS does have a distinct facial gestalt and phenotype that can be differentiated from KS. This growing AKS patient cohort also informs an emerging approach to management and health surveillance for these patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Au PYB, You J, Caluseriu O, Schwartzentruber J, Majewski J, Bernier FP, et al. GeneMatcher aids in the identification of a new malformation syndrome with intellectual disability, unique facial dysmorphisms, and skeletal and connective tissue abnormalities caused by de novo variants in HNRNPK. Hum Mutat. 2015;36:1009–14. doi: 10.1002/humu.22837. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dentici ML, Barresi S, Niceta M, Pantaleoni F, Pizzi S, Dallapiccola B, et al. Clinical spectrum of Kabuki-like syndrome caused by HNRNPK haploinsufficiency. Clin Genet. 2017;93:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

