Relativistic Doppler-boosted γ-rays in High Fields
- PMID: 29904181
- PMCID: PMC6002516
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-27122-9
Relativistic Doppler-boosted γ-rays in High Fields
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Relativistic Doppler-boosted γ-rays in High Fields.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 9;9(1):14777. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43378-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31594960 Free PMC article.
Abstract
The relativistic Doppler effect is one of the most famous implications of the principles of special relativity and is intrinsic to moving radiation sources, relativistic optics and many astrophysical phenomena. It occurs in the case of a plasma sail accelerated to relativistic velocities by an external driver, such as an ultra-intense laser pulse. Here we show that the relativistic Doppler effect on the high energy synchrotron photon emission (~10 MeV), strongly depends on two intrinsic properties of the plasma (charge state and ion mass) and the transverse extent of the driver. When the moving plasma becomes relativistically transparent to the driver, we show that the γ-ray emission is Doppler-boosted and the angular emission decreases; optimal for the highest charge-to-mass ratio ion species (i.e. a hydrogen plasma). This provides new fundamental insight into the generation of γ-rays in extreme conditions and informs related experiments using multi-petawatt laser facilities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

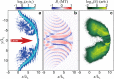

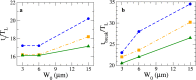

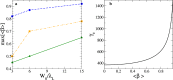
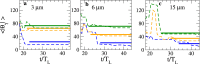
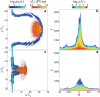
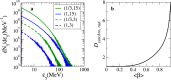
References
-
- Doviak, R. J. Doppler Radar and Weather Observations, 2nd ed. Dover Books on Engineering (2006).
-
- Bulanov SV, Naumova NM, Pegoraro F. Interaction of an ultrashort, relativistically strong laser pulse with an overdense plasma. Phys. Plasmas. 1994;1:745. doi: 10.1063/1.870766. - DOI
-
- Bulanov SV, et al. On the design of experiments for the study of extreme field limits in the interaction of laser with ultrarelativistic electron beam. Nucl. Inst. Meth. Phys. Res. A. 2011;660:31–42. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2011.09.029. - DOI
-
- Di Piazza A, Muller C, Hatsagortsyan KZ, Keitel CH. Extremely high-intensity laser interactions with fundamental quantum systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2012;84:1177. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.84.1177. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

