Role of DKK4 in Tumorigenesis and Tumor Progression
- PMID: 29904276
- PMCID: PMC6001654
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.24329
Role of DKK4 in Tumorigenesis and Tumor Progression
Abstract
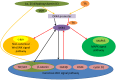
Tumor is the most public health problem. The Wnt signal pathway extensively participates in diverse progresses containing embryonic development, maintenance of homeostasis and tumor pathogenesis. The Wnt signal pathway consists of canonical signal pathway, noncanonical Wnt/PCP pathway and noncanonical Wnt/Ca2+ pathway. The deletion of the ligand of Wnts results in cytoplasmic β-catenin phosphorylation, stopping entry of β-catenin to nuclear in canonical Wnt signaling. Instead, binding of Wnts to frizzled (FZ/FZD) as well as LRP5/6 causes activation of Wnt signal pathways. This facilitates entry of β-catenin to nuclear. The Dickkopf proteins (DKKs) have been known as the antagonist of Wnt signal pathway. A number of research of DKK1, 2, 3 have been reported, however, the effect of DKK4 on tumor process is still mysterious. A more distinct comprehension about the effect of DKK4 on tumorigenesis and tumor process will shed light on biomedical research of DKK4 and tumor research. This review summarizes the current knowledge of DKK4 in various kinds of tumors.
Keywords: DKK4; Tumor; Wnt signal pathway; β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dickkopf 4 (DKK4) acts on Wnt/β-catenin pathway by influencing β-catenin in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncogene. 2012 Sep 20;31(38):4233-44. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.580. Epub 2012 Jan 16. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22249261
-
The effects of Dickkopf-4 on the proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis of osteoblasts.Endocrinology. 2013 Dec;154(12):4618-26. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1387. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 24105477
-
DICKKOPF-4 activates the noncanonical c-Jun-NH2 kinase signaling pathway while inhibiting the Wnt-canonical pathway in human renal cell carcinoma.Cancer. 2011 Apr 15;117(8):1649-60. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25666. Epub 2010 Nov 8. Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21472712 Free PMC article.
-
A literature review on function and regulation mechanism of DKK4.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Mar;25(6):2786-2794. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16372. Epub 2021 Feb 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33586359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic polymorphism in extracellular regulators of Wnt signaling pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:847529. doi: 10.1155/2015/847529. Epub 2015 Apr 5. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25945348 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrant accumulation of Dickkopf 4 promotes tumor progression via forming the immune suppressive microenvironment in gastrointestinal stromal tumor.Cancer Med. 2019 Sep;8(11):5352-5366. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2437. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31353847 Free PMC article.
-
A new risk model for CSTA, FAM83A, and MYCT1 predicts poor prognosis and is related to immune infiltration in lung squamous cell carcinoma.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Nov 15;14(11):7705-7725. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36505278 Free PMC article.
-
Cell communication and relevant signaling pathways in osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling.Bone Res. 2025 Apr 7;13(1):45. doi: 10.1038/s41413-025-00417-0. Bone Res. 2025. PMID: 40195313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer Stem Cell for Tumor Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 26;13(19):4814. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194814. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Clinical Significance of Dickkopf Wnt Signaling Pathway Inhibitor Gene Family in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Nov 26;26:e927368. doi: 10.12659/MSM.927368. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 33281184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barkell AM, Holdsworth G, Waters LC, Veverka V, Slocombe PM, Muskett FW. et al. Resonance assignment and secondary structure determination of full length human Dickkopf 4 (hDkk4), a secreted, disulphide-rich Wnt inhibitor protein. Biomolecular NMR assignments. 2015;9:147–51. doi:10.1007/s12104-014-9562-2. - PubMed
-
- Klaus A, Birchmeier W. Wnt signalling and its impact on development and cancer. Nature reviews Cancer. 2008;8:387–98. doi:10.1038/nrc2389. - PubMed
-
- Gao C, Chen YG. Dishevelled: The hub of Wnt signaling. Cellular signalling. 2010;22:717–27. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.11.021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

