Anabolic androgenic steroid-induced acute myocardial infarction with multiorgan failure
- PMID: 29904303
- PMCID: PMC5997056
- DOI: 10.1080/08998280.2018.1460130
Anabolic androgenic steroid-induced acute myocardial infarction with multiorgan failure
Abstract
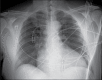
The abuse of anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS) has remained on the rise despite their well-known deleterious effects. We describe a case of AAS-induced multisystem failure following an extensive history of abuse in a 41-year-old bodybuilder. Furthermore, we review pertinent literature and discuss the different pathophysiologic mechanisms through which AAS affect the heart and other organs. This case points to the possibility of multiorgan involvement and severe cardiac effects of AAS abuse in young individuals who may not have any past medical history.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; acute myocardial infarction; anabolic steroid abuse; multiorgan failure; subclinical congestive heart failure; testosterone replacement therapy.
Figures
References
-
- O'Sullivan AJ, Kennedy MC, Casey JH, Day RO, Corrigan B, Wodak AD. Anabolic–androgenic steroids: medical assessment of present, past and potential users. Med J Aust. 2000;173:323–327. PMID:11061405. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous