Dysregulation of B Cell Activity During Proliferative Kidney Disease in Rainbow Trout
- PMID: 29904385
- PMCID: PMC5990594
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01203
Dysregulation of B Cell Activity During Proliferative Kidney Disease in Rainbow Trout
Abstract
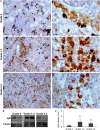
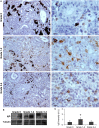
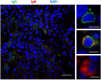
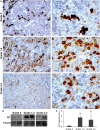
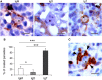
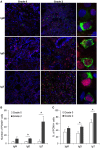
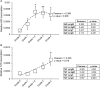
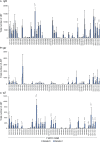
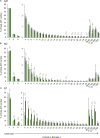
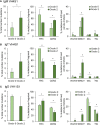
Proliferative kidney disease (PKD) is a widespread disease caused by the endoparasite Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (Myxozoa: Malacosporea). Clinical disease, provoked by the proliferation of extrasporogonic parasite stages, is characterized by a chronic kidney pathology with underlying transcriptional changes indicative of altered B cell responses and dysregulated T-helper cell-like activities. Despite the relevance of PKD to European and North American salmonid aquaculture, no studies, to date, have focused on further characterizing the B cell response during the course of this disease. Thus, in this work, we have studied the behavior of diverse B cell populations in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) naturally infected with T. bryosalmonae at different stages of preclinical and clinical disease. Our results show a clear upregulation of all trout immunoglobulins (Igs) (IgM, IgD, and IgT) demonstrated by immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis, suggesting the alteration of diverse B cell populations that coexist in the infected kidney. Substantial changes in IgM, IgD, and IgT repertoires were also identified throughout the course of the disease further pointing to the involvement of the three Igs in PKD through what appear to be independently regulated mechanisms. Thus, our results provide strong evidence of the involvement of IgD in the humoral response to a specific pathogen for the first time in teleosts. Nevertheless, it was IgT, a fish-specific Ig isotype thought to be specialized in mucosal immunity, which seemed to play a prevailing role in the kidney response to T. bryosalmonae. We found that IgT was the main Ig coating extrasporogonic parasite stages, IgT+ B cells were the main B cell subset that proliferated in the kidney with increasing kidney pathology, and IgT was the Ig for which more significant changes in repertoire were detected. Hence, although our results demonstrate a profound dysregulation of different B cell subsets during PKD, they point to a major involvement of IgT in the immune response to the parasite. These results provide further insights into the pathology of PKD that may facilitate the future development of control strategies.
Keywords: B cells; Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae; immunoglobulin D; immunoglobulin M; immunoglobulin T; proliferative kidney disease; rainbow trout.
Figures
References
-
- Hedrick RP, Macconnell E, De Kinkelin P. Proliferative kidney disease of salmonid fish. Annu Rev Fish Dis (1993) 3:277–90. 10.1016/0959-8030(93)90039-E - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

