Ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir + dasabuvir + ribavirin in HCV genotype 1 infected patients who failed previous protease inhibitor therapy
- PMID: 29904724
- PMCID: PMC6000745
- DOI: 10.5114/ceh.2018.75957
Ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir + dasabuvir + ribavirin in HCV genotype 1 infected patients who failed previous protease inhibitor therapy
Abstract
Aim of the study: Combination of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir + dasabuvir ± ribavirin (3DDA±RBV) therapy is shown to be effective in HCV genotype 1 (GT1) infected patients. However, sparse data exist in patients who failed previous boceprevir or telaprevir based therapies. Real life efficacy and safety of this combination were evaluated in HCV GT1b infected patients (mostly cirrhotics) with compensated liver disease who failed previous boceprevir or telaprevir based therapies more than a year before.
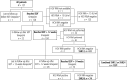
Material and methods: Data of previous protease inhibitor failure patients, treated with 3DAA+RBV for 12 weeks (GT1b and/or non-cirrhotics) or 24 weeks (non-GT1b cirrhotics), were retrospectively collected.
Results: Population characteristics: boceprevir/telaprevir-failure: 82/45, GT1b: 117, cirrhotic: 111 (87.4%). SVR12/24 was observed in 103/105 patients (98.1%) of those who reached either time point. Four SAEs reported: one death due to myocardial infarction, another due to recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after achieving SVR12, two hospitalizations (elevation of transaminases, pneumonia). Grade ≥ 3 AEs or laboratory abnormalities were reported in < 10% of patients; they were transient in all patients. No early discontinuation of drugs due to SAE has been reported.
Conclusions: One year after previous failure of boceprevir or telaprevir based therapy, 12 weeks of 3DAA+RBV combination in HCV GT1b infected patients is similarly effective and safe as in those with no previous HCV therapy, even in the presence of cirrhosis. These findings might be of particular interest in settings where alternative therapies for such patients are not available or not affordable.
Keywords: cirrhosis; direct acting antiviral drugs; hepatitis C virus; protease inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA) Victrelis. Summary of product characteristics. Updated: 23/06/2016. Available from: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Info....
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA) Incivo. Summary of product characteristics. Updated: 06/10/2016. Available from: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Info....
-
- Sullivan JC, De Meyer S, Bartels DJ, et al. Evolution of treatment-emergent resistant variants in telaprevir phase 3 clinical trials. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:221–229. - PubMed
-
- Howe AY, Long J, Nickle D, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients receiving boceprevir for treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Antiviral Res. 2015;113:71–78. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
