Crucial role for Nox2 and sleep deprivation in aircraft noise-induced vascular and cerebral oxidative stress, inflammation, and gene regulation
- PMID: 29905797
- PMCID: PMC6174027
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy333
Crucial role for Nox2 and sleep deprivation in aircraft noise-induced vascular and cerebral oxidative stress, inflammation, and gene regulation
Abstract
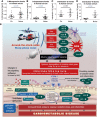
Aims: Aircraft noise causes endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Transportation noise increases the incidence of coronary artery disease, hypertension, and stroke. The underlying mechanisms are not well understood. Herein, we investigated effects of phagocyte-type NADPH oxidase (Nox2) knockout and different noise protocols (around-the-clock, sleep/awake phase noise) on vascular and cerebral complications in mice.
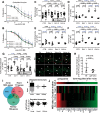
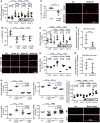
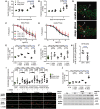
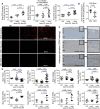
Methods and results: C57BL/6j and Nox2-/- (gp91phox-/-) mice were exposed to aircraft noise (maximum sound level of 85 dB(A), average sound pressure level of 72 dB(A)) around-the-clock or during sleep/awake phases for 1, 2, and 4 days. Adverse effects of around-the-clock noise on the vasculature and brain were mostly prevented by Nox2 deficiency. Around-the-clock aircraft noise of the mice caused the most pronounced vascular effects and dysregulation of Foxo3/circadian clock as revealed by next generation sequencing (NGS), suggesting impaired sleep quality in exposed mice. Accordingly, sleep but not awake phase noise caused increased blood pressure, endothelial dysfunction, increased markers of vascular/systemic oxidative stress, and inflammation. Noise also caused cerebral oxidative stress and inflammation, endothelial and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (e/nNOS) uncoupling, nNOS mRNA and protein down-regulation, and Nox2 activation. NGS revealed similarities in adverse gene regulation between around-the-clock and sleep phase noise. In patients with established coronary artery disease, night-time aircraft noise increased oxidative stress, and inflammation biomarkers in serum.
Conclusion: Aircraft noise increases vascular and cerebral oxidative stress via Nox2. Sleep deprivation and/or fragmentation caused by noise triggers vascular dysfunction. Thus, preventive measures that reduce night-time aircraft noise are warranted.
Figures

Comment in
-
Nocturnal noise knocks NOS by Nox: mechanisms underlying cardiovascular dysfunction in response to noise pollution.Eur Heart J. 2018 Oct 7;39(38):3540-3542. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy431. Eur Heart J. 2018. PMID: 30295761 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Ablation of lysozyme M-positive cells prevents aircraft noise-induced vascular damage without improving cerebral side effects.Basic Res Cardiol. 2021 Apr 30;116(1):31. doi: 10.1007/s00395-021-00869-5. Basic Res Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33929610 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of noise on vascular function, oxidative stress, and inflammation: mechanistic insight from studies in mice.Eur Heart J. 2017 Oct 1;38(37):2838-2849. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx081. Eur Heart J. 2017. PMID: 28329261 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigation of aircraft noise-induced vascular dysfunction and oxidative stress by exercise, fasting, and pharmacological α1AMPK activation: molecular proof of a protective key role of endothelial α1AMPK against environmental noise exposure.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2023 Oct 26;30(15):1554-1568. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwad075. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37185661
-
Oxidative stress and inflammation contribute to traffic noise-induced vascular and cerebral dysfunction via uncoupling of nitric oxide synthases.Redox Biol. 2020 Jul;34:101506. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101506. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32371009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental Noise and the Cardiovascular System.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Feb 13;71(6):688-697. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.12.015. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29420965 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Reciprocal Interactions Between Sleep Disorders and Parkinson's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2021 Feb 10;14:592989. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.592989. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33642969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep duration, daytime napping, and risk of incident stroke: Nuances by metabolic syndrome from the China health and retirement longitudinal study.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Sep 2;9:976537. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.976537. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36119748 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of lysozyme M-positive cells prevents aircraft noise-induced vascular damage without improving cerebral side effects.Basic Res Cardiol. 2021 Apr 30;116(1):31. doi: 10.1007/s00395-021-00869-5. Basic Res Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33929610 Free PMC article.
-
The Cardiovascular Effects of Noise.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Apr 5;116(14):245-250. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0245. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019. PMID: 31092312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Persistent Noise Exposure under Inflammatory Conditions.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jul 19;11(14):2067. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11142067. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Munzel T, Sorensen M, Gori T, Schmidt FP, Rao X, Brook J, Chen LC, Brook RD, Rajagopalan S.. Environmental stressors and cardio-metabolic disease: part I-epidemiologic evidence supporting a role for noise and air pollution and effects of mitigation strategies. Eur Heart J 2017;38:550–556. - PubMed
-
- Vienneau D, Schindler C, Perez L, Probst-Hensch N, Röösli M.. The relationship between transportation noise exposure and ischemic heart disease: a meta-analysis. Environ Res 2015;138:372–380. - PubMed
-
- Munzel T, Schmidt FP, Steven S, Herzog J, Daiber A, Sorensen M.. Environmental noise and the cardiovascular system. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018;71:688–697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

