5-Formylcytosine mediated DNA-protein cross-links block DNA replication and induce mutations in human cells
- PMID: 29905846
- PMCID: PMC6061883
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky444
5-Formylcytosine mediated DNA-protein cross-links block DNA replication and induce mutations in human cells
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: 5-Formylcytosine mediated DNA-protein cross-links block DNA replication and induce mutations in human cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Oct 12;46(18):9892. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky809. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30184121 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
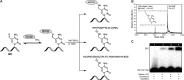
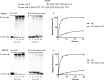
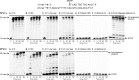
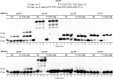
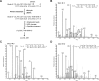
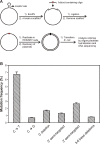
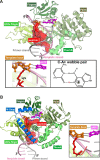
5-Formylcytosine (5fC) is an epigenetic DNA modification introduced via TET protein-mediated oxidation of 5-methyl-dC. We recently reported that 5fC form reversible DNA-protein conjugates (DPCs) with histone proteins in living cells (Ji et al. (2017) Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 56:14130-14134). We now examined the effects of 5fC mediated DPCs on DNA replication. Synthetic DNA duplexes containing site-specific DPCs between 5fC and lysine-containing proteins and peptides were subjected to primer extension experiments in the presence of human translesion synthesis DNA polymerases η and κ. We found that DPCs containing histones H2A or H4 completely inhibited DNA replication, but the replication block was removed when the proteins were subjected to proteolytic digestion. Cross-links to 11-mer or 31-mer peptides were bypassed by both polymerases in an error-prone manner, inducing targeted C→T transitions and -1 deletions. Similar types of mutations were observed when plasmids containing 5fC-peptide cross-links were replicated in human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293T cells. Molecular simulations of the 11-mer peptide-dC cross-links bound to human polymerases η and κ revealed that the peptide fits well on the DNA major groove side, and the modified dC forms a stable mismatch with incoming dATP via wobble base pairing in the polymerase active site.
Figures
References
-
- Barker S., Weinfeld M., Murray D.. DNA–protein crosslinks: their induction, repair, and biological consequences. Mutat. Res. 2005; 589:111–135. - PubMed
-
- Ide H., Shoulkamy M.I., Nakano T., Miyamoto-Matsubara M., Salem A.M.H.. Repair and biochemical effects of DNA–protein crosslinks. Mutat. Res. 2011; 711:113–122. - PubMed
-
- Barker S., Weinfeld M., Zheng J., Li L., Murray D.. Identification of mammalian proteins cross-linked to DNA by ionizing radiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005; 280:33826–33838. - PubMed
-
- Speit G., Schütz P., Merk O.. Induction and repair of formaldehyde-induced DNA–protein crosslinks in repair-deficient human cell lines. Mutagenesis. 2000; 15:85–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

