Physiological and unappreciated roles of CaMKII in the heart
- PMID: 29905892
- PMCID: PMC6003982
- DOI: 10.1007/s00395-018-0688-8
Physiological and unappreciated roles of CaMKII in the heart
Abstract
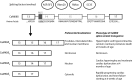
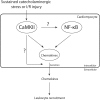
In the cardiomyocyte, CaMKII has been identified as a nodal influencer of excitation-contraction and also excitation-transcription coupling. Its activity can be regulated in response to changes in intracellular calcium content as well as after several post-translational modifications. Some of the effects mediated by CaMKII may be considered adaptive, while effects of sustained CaMKII activity may turn into the opposite and are detrimental to cardiac integrity and function. As such, CaMKII has long been noted as a promising target for pharmacological inhibition, but the ubiquitous nature of CaMKII has made it difficult to target CaMKII specifically where it is detrimental. In this review, we provide a brief overview of the physiological and pathophysiological properties of CaMKII signaling, but we focus on the physiological and adaptive functions of CaMKII. Furthermore, special consideration is given to the emerging role of CaMKII as a mediator of inflammatory processes in the heart.
Keywords: Apoptosis; CaMKII; Calcium; Calmodulin; Cardiomyocyte; Inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Backs J, Backs T, Neef S, Kreusser MM, Lehmann LH, Patrick DM, Grueter CE, Qi X, Richardson JA, Hill JA, Katus HA, Bassel-Duby R, Maier LS, Olson EN. The delta isoform of CaM kinase II is required for pathological cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling after pressure overload. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:2342–2347. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

