Activation recovery interval imaging of premature ventricular contraction
- PMID: 29906289
- PMCID: PMC6003683
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196916
Activation recovery interval imaging of premature ventricular contraction
Abstract
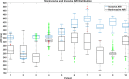
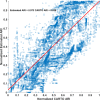
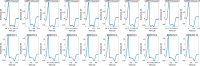
Dispersion of ventricular repolarization due to abnormal activation contributes to the susceptibility to cardiac arrhythmias. However, the global pattern of repolarization is difficult to assess clinically. Activation recovery interval (ARI) has been used to understand the properties of ventricular repolarization. In this study, we developed an ARI imaging technique to noninvasively reconstruct three-dimensional (3D) ARI maps in 10 premature ventricular contraction (PVC) patients and evaluated the results with the endocardial ARI maps recorded by a clinical navigation system (CARTO). From the analysis results of a total of 100 PVC beats in 10 patients, the average correlation coefficient is 0.86±0.05 and the average relative error is 0.06±0.03. The average localization error is 4.5±2.3 mm between the longest ARI sites in 3D ARI maps and those in CARTO endocardial ARI maps. The present results suggest that ARI imaging could serve as an alternative of evaluating global pattern of ventricular repolarization noninvasively and could assist in the future investigation of the relationship between global repolarization dispersion and the susceptibility to cardiac arrhythmias.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Laurita KR, Girouard SD, Akar FG, Rosenbaum DS. Modulated dispersion explains changes in arrhythmia vulnerability during premature stimulation of the heart. Circulation. 1998;98: 2774–2780. - PubMed
-
- Han J, Moe GK. Nonuniform recovery of excitability in ventricular muscle. Circ Res. 1964;14: 44–60. - PubMed
-
- Han J, Millet D, Chizzonitti B, Moe GK. Temporal dispersion of recovery of excitability in atrium and ventricle as a function of heart rate. Am Heart J. 1966;71: 481–487. - PubMed
-
- Chauhan VS, Downar E, Nanthakumar K, Parker JD, Ross HJ, Chan W, et al. Increased ventricular repolarization heterogeneity in patients with ventricular arrhythmia vulnerability and cardiomyopathy: a human in vivo study. Am J Physiol-Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;290: H79–H86. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00648.2005 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

