Effects of 8-week sensory electrical stimulation combined with motor training on EEG-EMG coherence and motor function in individuals with stroke
- PMID: 29907780
- PMCID: PMC6003966
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-27553-4
Effects of 8-week sensory electrical stimulation combined with motor training on EEG-EMG coherence and motor function in individuals with stroke
Abstract
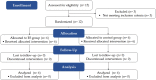
The peripheral sensory system is critical to regulating motor plasticity and motor recovery. Peripheral electrical stimulation (ES) can generate constant and adequate sensory input to influence the excitability of the motor cortex. The aim of this proof of concept study was to assess whether ES prior to each hand function training session for eight weeks can better improve neuromuscular control and hand function in chronic stroke individuals and change electroencephalography-electromyography (EEG-EMG) coherence, as compared to the control (sham ES). We recruited twelve subjects and randomly assigned them into ES and control groups. Both groups received 20-minute hand function training twice a week, and the ES group received 40-minute ES on the median nerve of the affected side before each training session. The control group received sham ES. EEG, EMG and Fugl-Meyer Assessment (FMA) were collected at four different time points. The corticomuscular coherence (CMC) in the ES group at fourth weeks was significantly higher (p = 0.004) as compared to the control group. The notable increment of FMA at eight weeks and follow-up was found only in the ES group. The eight-week rehabilitation program that implemented peripheral ES sessions prior to function training has a potential to improve neuromuscular control and hand function in chronic stroke individuals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Investigating the Effects of Peripheral Electrical Stimulation on Corticomuscular Functional Connectivity Stroke Survivors.Top Stroke Rehabil. 2016 Jun;23(3):154-62. doi: 10.1080/10749357.2015.1122264. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2016. PMID: 27077975
-
Intramuscular electrical stimulation for upper limb recovery in chronic hemiparesis: an exploratory randomized clinical trial.Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009 Jul-Aug;23(6):569-78. doi: 10.1177/1545968308328729. Epub 2009 Jan 20. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009. PMID: 19155351 Clinical Trial.
-
Wrist Rehabilitation Assisted by an Electromyography-Driven Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Robot After Stroke.Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2015 Sep;29(8):767-76. doi: 10.1177/1545968314565510. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2015. PMID: 25549656 Clinical Trial.
-
Brain plasticity and rehabilitation in stroke patients.J Nippon Med Sch. 2015;82(1):4-13. doi: 10.1272/jnms.82.4. J Nippon Med Sch. 2015. PMID: 25797869 Review.
-
Impact of sensory integration training on balance among stroke patients: sensory integration training on balance among stroke patients.Open Med (Wars). 2016 Aug 13;11(1):330-335. doi: 10.1515/med-2016-0061. eCollection 2016. Open Med (Wars). 2016. PMID: 28352817 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Narrative Review on Multi-Domain Instrumental Approaches to Evaluate Neuromotor Function in Rehabilitation.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Aug 13;11(16):2282. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11162282. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37628480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroplasticity after upper-extremity rehabilitation therapy with sensory stimulation in chronic stroke survivors.Brain Commun. 2022 Jul 24;4(4):fcac191. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac191. eCollection 2022. Brain Commun. 2022. PMID: 35938072 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Use of EMG and EEG Techniques for Neuromotor Assessment in Rehabilitative Applications: A Systematic Review.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Oct 22;21(21):7014. doi: 10.3390/s21217014. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34770320 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Efficacy of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Acupoints on Motor and Neural Recovery of the Affected Upper Extremity in Chronic Stroke: A Sham-Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 May 20;9(5):614. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9050614. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34065465 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Neurostimulations for Upper Extremity Function Recovery after Stroke: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 19;11(20):6162. doi: 10.3390/jcm11206162. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36294485 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cengić L, Vuletić V, Karlić M, Dikanović M, Demarin V. Motor and cognitive impairment after stroke. Acta Clin. Croat. 2011;50:463–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

