Results of next-generation sequencing gene panel diagnostics including copy-number variation analysis in 810 patients suspected of heritable thoracic aortic disorders
- PMID: 29907982
- PMCID: PMC6175145
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.23565
Results of next-generation sequencing gene panel diagnostics including copy-number variation analysis in 810 patients suspected of heritable thoracic aortic disorders
Abstract
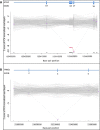
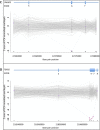
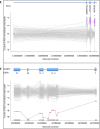
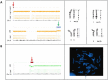
Simultaneous analysis of multiple genes using next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology has become widely available. Copy-number variations (CNVs) in disease-associated genes have emerged as a cause for several hereditary disorders. CNVs are, however, not routinely detected using NGS analysis. The aim of this study was to assess the diagnostic yield and the prevalence of CNVs using our panel of Hereditary Thoracic Aortic Disease (H-TAD)-associated genes. Eight hundred ten patients suspected of H-TAD were analyzed by targeted NGS analysis of 21 H-TAD associated genes. In addition, the eXome hidden Markov model (XHMM; an algorithm to identify CNVs in targeted NGS data) was used to detect CNVs in these genes. A pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant was found in 66 of 810 patients (8.1%). Of these 66 pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants, six (9.1%) were CNVs not detectable by routine NGS analysis. These CNVs were four intragenic (multi-)exon deletions in MYLK, TGFB2, SMAD3, and PRKG1, respectively. In addition, a large duplication including NOTCH1 and a large deletion encompassing SCARF2 were detected. As confirmed by additional analyses, both CNVs indicated larger chromosomal abnormalities, which could explain the phenotype in both patients. Given the clinical relevance of the identification of a genetic cause, CNV analysis using a method such as XHMM should be incorporated into the clinical diagnostic care for H-TAD patients.
Keywords: copy-number variations; eXome hidden Markov model; genetics; thoracic aortic aneurysm; thoracic aortic dissection.
© 2018 The Authors. Human Mutation published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Ackerman, M. J. , Priori, S. G. , Willems, S. , Berul, C. , Brugada, R. , Calkins, H. , … European Heart Rhythm, A. (2011). HRS/EHRA expert consensus statement on the state of genetic testing for the channelopathies and cardiomyopathies: This document was developed as a partnership between the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) and the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA). Europace, 13(8), 1077–1109. 10.1093/europace/eur245 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Akutsu, K. , Morisaki, H. , Takeshita, S. , Sakamoto, S. , Tamori, Y. , Yoshimuta, T. , … Morisaki, T. (2007). Phenotypic heterogeneity of Marfan‐like connective tissue disorders associated with mutations in the transforming growth factor‐beta receptor genes. Circulation Journal, 71(8), 1305–1309. - PubMed
-
- Amarillo, I. E. , O'Connor, S. , Lee, C. K. , Willing, M. , & Wambach, J. A. (2015). De novo 9q gain in an infant with tetralogy of Fallot with absent pulmonary valve: Patient report and review of congenital heart disease in 9q duplication syndrome. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A, 167A(12), 2966–2974. 10.1002/ajmg.a.37296 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arbustini, E. , Grasso, M. , Ansaldi, S. , Malattia, C. , Pilotto, A. , Porcu, E. , … Tavazzi, L. (2005). Identification of sixty‐two novel and twelve known FBN1 mutations in eighty‐one unrelated probands with Marfan syndrome and other fibrillinopathies. Human Mutation, 26(5), 494 10.1002/humu.9377 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

