A complex interplay between the extracellular matrix and the innate immune response to microbial pathogens
- PMID: 29908065
- PMCID: PMC6142291
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12972
A complex interplay between the extracellular matrix and the innate immune response to microbial pathogens
Abstract
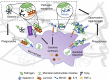
The role of the host extracellular matrix (ECM) in infection tends to be neglected. However, the complex interactions between invading pathogens, host tissues and immune cells occur in the context of the ECM. On the pathogen side, a variety of surface and secreted molecules, including microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules and tissue-degrading enzymes, are employed that interact with different ECM proteins to effectively establish an infection at specific sites. Microbial pathogens can also hijack or misuse host proteolytic systems to modify the ECM, evade immune responses or process biologically active molecules such as cell surface receptors and cytokines that direct cell behaviour and immune defence. On the host side, the ECM composition and three-dimensional ultrastructure undergo significant modifications, which have a profound impact on the specific signals that the ECM conveys to immune cells at the forefront of infection. Unexpectedly, activated immune cells participate in the remodelling of the local ECM by synthesizing ECM glycoproteins, proteoglycans and collagen molecules. The close interplay between the ECM and the innate immune response to microbial pathogens ultimately affects the outcome of infection. This review explores and discusses recent data that implicate an active role for the ECM in the immune response to infection, encompassing antimicrobial activities, microbial recognition, macrophage activation, phagocytosis, leucocyte population balance, and transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of inflammatory networks, and may foster novel antimicrobial approaches.
Keywords: extracellular matrix; immunity; infection.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Pizarro‐Cerda J, Cossart P. Bacterial adhesion and entry into host cells. Cell 2006; 124:715–27. - PubMed
-
- Kuusela P. Fibronectin binds to Staphylococcus aureus . Nature 1978; 276:718–20. - PubMed
-
- Chagnot C, Listrat A, Astruc T, Desvaux M. Bacterial adhesion to animal tissues: protein determinants for recognition of extracellular matrix components. Cell Microbiol 2012; 14:1687–96. - PubMed
-
- Sorokin L. The impact of the extracellular matrix on inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 2010; 10:712–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

