A comparison of biofluid cytokine markers across platform technologies: Correspondence or divergence?
- PMID: 29908923
- PMCID: PMC6289877
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.05.032
A comparison of biofluid cytokine markers across platform technologies: Correspondence or divergence?
Abstract
Background: Quantification of biofluid cytokines is a rapidly growing area of translational research. However, comparability across the expanding number of available assay platforms for detection of the same proteins remains to be determined. We aimed to directly compare a panel of commonly measured cytokines in plasma of typically aging adults across two high sensitivity quantification platforms, Meso Scale Discovery high performance electrochemiluminiscence (HPE) and single-molecule immunosorbent assays (Simoa) by Quanterix.
Methods: 57 community-dwelling older adults completed a blood draw, neuropsychological assessment, and brain MRI as part of a healthy brain aging study. Plasma samples from the same draw dates were analyzed for IL-10, IP-10, IL-6, TNFα, and IL-1β on HPE and Simoa, separately. Reliable detectability (coefficient of variance (CV) < 20% and outliers 3 interquartiles above the median removed), intra-assay precision, absolute concentrations, reproducibility across platforms, and concurrent associations with external variables of interest (e.g., demographics, peripheral markers of vascular health, and brain health) were examined.
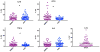
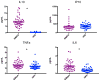
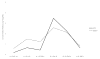
Results: The proportion of cytokines reliably measured on HPE (87.7-93.0%) and Simoa (75.4-93.0%) did not differ (ps > 0.32), with the exception of IL-1β which was only reliably measured using Simoa (68.4%). On average, CVs were acceptable at <8% across both platforms. Absolute measured concentrations were higher using Simoa for IL-10, IL-6, and TNFα (ps < 0.05). HPE and Simoa shared only small-to-moderate proportions of variance with one another on the same cytokine proteins (range: r = 0.26 for IL-10 to r = 0.64 for IL-6), though platform agreement did not dependent on cytokine concentrations. Cytokine ratios within each platform demonstrated similar relative patterns of up- and down-regulation across HPE and Simoa, though still significantly differed (ps < 0.001). Supporting concurrent validity, all 95% confidence intervals of the correlations between cytokines and external variables overlapped between the two platforms. Moreover, most associations were in expected directions and consistently so across platforms (e.g., IL-6 and TNFα), though with several notable exceptions for IP-10 and IL-10.
Conclusions: HPE and Simoa showed comparable detectability and intra-assay precision measuring a panel of commonly examined cytokine proteins, with the exception of IL-1β which was not reliably detected on HPE. However, Simoa demonstrated overall higher concentrations and the two platforms did not show agreement when directly compared against one another. Relative cytokine ratios and associations demonstrated similar patterns across platforms. Absolute cytokine concentrations may not be directly comparable across platforms, may be analyte dependent, and interpretation may be best limited to discussion of relative associations.
Keywords: Immune activation; Meso Scale Discovery; Plasma markers; Quanterix; Typical aging.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
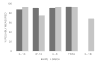


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

