Impact of early institutionalization on attention mechanisms underlying the inhibition of a planned action
- PMID: 29908954
- PMCID: PMC6205198
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.06.008
Impact of early institutionalization on attention mechanisms underlying the inhibition of a planned action
Abstract
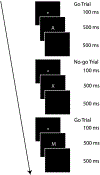
Institutional rearing is associated with deficits in executive functions, such as inhibitory control, and may contribute to later externalizing behavior problems. In the current study, we explored the impact of institutional rearing on attention in the context of inhibiting a planned action. As part of the Bucharest Early Intervention Project (BEIP), children were randomized to either remain in the institutions in which they lived (Care as Usual Group) or be placed into foster family homes (Foster Care Group). We also recruited age and gender matched never-institutionalized (NIG) children from the Bucharest community. We examined differences in behavioral and Event Related Potentials (ERPs) during a go-no-go task when children were 12 years old. Results revealed that the ever-institutionalized group (CAUG and FCG combined) showed slower reaction times, worse performance accuracy, larger P2 activation, and smaller (less negative) N2 activation than the NIG group. Results of a moderation analysis revealed that children who spent more time in institutions and had small N2s showed more externalizing symptoms. These results have implications for the design of treatment approaches for previously institutionalized children with externalizing behavior problems.
Keywords: BEIP; Early institutionalization; Event-related potentials; Externalizing behavior; Inhibiting a planned action.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deficits in error monitoring are associated with externalizing but not internalizing behaviors among children with a history of institutionalization.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2016 Oct;57(10):1145-53. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12604. Epub 2016 Aug 29. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27569003 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Early adversity and neural correlates of executive function: implications for academic adjustment.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2012 Feb 15;2 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2011.09.008. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22682911 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Foster Care Intervention on Trajectories of General and Specific Psychopathology Among Children With Histories of Institutional Rearing: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Psychiatry. 2018 Nov 1;75(11):1137-1145. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.2556. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30267045 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Psychiatric outcomes in young children with a history of institutionalization.Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2011 Jan-Feb;19(1):15-24. doi: 10.3109/10673229.2011.549773. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21250893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroencephalogram activity related to psychopathological and neuropsychological symptoms in institutionalised minors: a systematic review.Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2025 May 8;37:e62. doi: 10.1017/neu.2025.19. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2025. PMID: 40336208
Cited by
-
Neural and Cognitive Factors Influencing the Emergence of Psychopathology: Insights From the Bucharest Early Intervention Project.Child Dev Perspect. 2018 Mar;12(1):28-33. doi: 10.1111/cdep.12251. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Child Dev Perspect. 2018. PMID: 29531577 Free PMC article.
-
Global deficits in executive functioning are transdiagnostic mediators between severe childhood neglect and psychopathology in adolescence.Psychol Med. 2020 Jul;50(10):1687-1694. doi: 10.1017/S0033291719001764. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Psychol Med. 2020. PMID: 31391139 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of early life adversity on children's mental health and cognitive functioning.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Jun 10;12(1):244. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-02001-0. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35688817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What was learned from studying the effects of early institutional deprivation.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2021 Nov;210:173272. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2021.173272. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2021. PMID: 34509501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative urgency as a risk factor for hazardous alcohol use: Dual influences of cognitive control and reinforcement processing.Neuropsychologia. 2021 Oct 15;161:108009. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2021.108009. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Neuropsychologia. 2021. PMID: 34454939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiken LS, West SG, & Reno RR (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Sage.
-
- Bocquillon P, Bourriez JL, Palmero-Soler E, Molaee-Ardekani B, Derambure P, & Dujardin K (2014). The spatiotemporal dynamics of early attention processes: a high-resolution electroencephalographic study of N2 subcomponent sources. Neuroscience, 271, 9–22. - PubMed
-
- Bartholow BD, Pearson MA, Dickter CL, Sher KJ, Fabiani M, & Gratton G (2005). Strategic control and medial frontal negativity: Beyond errors and response conflict. Psychophysiology, 42(1), 33–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

