Genetic Regulation of Plasma Lipid Species and Their Association with Metabolic Phenotypes
- PMID: 29909275
- PMCID: PMC6397773
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cels.2018.05.009
Genetic Regulation of Plasma Lipid Species and Their Association with Metabolic Phenotypes
Abstract
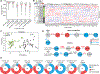
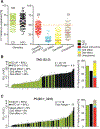
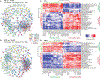
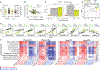
The genetic regulation and physiological impact of most lipid species are unexplored. Here, we profiled 129 plasma lipid species across 49 strains of the BXD mouse genetic reference population fed either chow or a high-fat diet. By integrating these data with genomics and phenomics datasets, we elucidated genes by environment (diet) interactions that regulate systemic metabolism. We found quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for ∼94% of the lipids measured. Several QTLs harbored genes associated with blood lipid levels and abnormal lipid metabolism in human genome-wide association studies. Lipid species from different classes provided signatures of metabolic health, including seven plasma triglyceride species that associated with either healthy or fatty liver. This observation was further validated in an independent mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and in plasma from NAFLD patients. This work provides a resource to identify plausible genes regulating the measured lipid species and their association with metabolic traits.
Keywords: BXD; TAG,; fatty liver,; genetic reference population, GRP,; genetic variation; lipid species; lipidomics; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, NAFLD,; quantitative trait locus, QTL,; steatosis,.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Belknap JK (1998). Effect of within-strain sample size on QTL detection and mapping using recombinant inbred mouse strains. Behav. Genet 28, 29–38. - PubMed
-
- Broman KW, Wu H, Sen S, and Churchill GA (2003). R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19, 889–890. - PubMed
-
- Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC, Grundy SM, and Hobbs HH (2004). Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology 40, 1387–1395. - PubMed
-
- Dewey FE, Murray MF, Overton JD, Habegger L, Leader JB, Fetterolf SN, O’Dushlaine C, Van Hout CV, Staples J, Gonzaga-Jauregui C, et al. (2016). Distribution and clinical impact of functional variants in 50,726 whole-exome sequences from the DiscovEHR study. Science 354, 10.1126/science.aaf6814. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Diabetes Genetics Initiative of Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT Lund University and Novartis Institutes of BioMedical Research, Saxena R, Voight BF, Lyssenko V, Burtt NP, de Bakker PI, Chen H, Roix JJ, Kathiresan S, Hirschhorn JN, et al. (2007). Genome-wide association analysis identifies loci for type 2 diabetes and triglyceride levels. Science 316, 1331–1336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

