Effects of electroacupuncture on bladder and bowel function in patients with transverse myelitis: a prospective observational study
- PMID: 29909400
- PMCID: PMC6089199
- DOI: 10.1136/acupmed-2016-011225
Effects of electroacupuncture on bladder and bowel function in patients with transverse myelitis: a prospective observational study
Abstract
Objective: To preliminarily explore the effect of electroacupuncture (EA) on bladder and bowel dysfunction in patients with transverse myelitis.
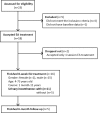
Methods: Sixteen participants were treated with EA at bilateral BL32, BL33, and BL35 once a day, five times a week for the first 4 weeks, and once every other day, three times a week for the following 4 weeks. Patients were then followed up for 6 months. Bladder and bowel function, and the safety of EA, were assessed.
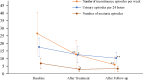
Results: After 8 weeks of treatment, five (5/16, 31%) patients resumed normal voiding, three (6/16, 38%) regained partially normal voiding, and five (5/16, 31%) had no change. After treatment, the residual urine volume decreased by 100 mL (IQR 53-393 mL; P<0.05) in nine patients with bladder voiding dysfunction; in 11 patients with urinary incontinence, the number of weekly urinary incontinence episodes, 24-hour urinary episodes, and nocturia episodes per night diminished by 14 (95% CI 5 to 22), 5 (95% CI 1 to 9), and 4 (95% CI 0 to 7) episodes, respectively (all P<0.05). After 8 weeks of treatment in eight patients with faecal retention, four (4/8, 50%) resumed normal bowel movements, three (3/8, 38%) regained partially normal bowel movements, and one (1/8, 13%) had no change.
Conclusions: EA might be a promising alternative for the management of bladder and bowel dysfunction in patients with transverse myelitis. Randomised controlled trials are needed to confirm the effectiveness and safety of EA for this condition.
Keywords: electroacupuncture; neurology; spine; urology.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

