Anderson-Fabry disease in heart failure
- PMID: 29909504
- PMCID: PMC6082315
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-018-0432-5
Anderson-Fabry disease in heart failure
Abstract
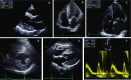
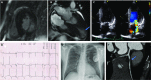
Anderson-Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder caused by mutations in the GLA gene that result in deficiency of the enzyme alpha-galactosidase A. The worldwide incidence of Fabry's disease is reported to be in the range of 1 in 40,000-117,000, although this value may be a significant underestimate given under recognition of symptoms and delayed or missed diagnosis. Deficiency in alpha-galactosidase A causes an accumulation of neutral glycosphingolipids such as globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) in lysosomes within various tissues including the vascular endothelium, kidneys, heart, eyes, skin and nervous system. Gb3 accumulation induces pathology via the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, growth-promoting factors and by oxidative stress, resulting in myocardial extracellular matrix remodelling, left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), vascular dysfunction and interstitial fibrosis. Cardiac involvement manifesting as ventricular hypertrophy, systolic and diastolic dysfunction, valvular abnormalities and conduction tissue disease is common in AFD and is associated with considerable cardiovascular morbidity and mortality from heart failure, sudden cardiac death and stroke-related death.
Keywords: Anderson-Fabry disease; GLA gene; Globotriaosylceramide; Heart failure.
Conflict of interest statement
Perry Elliott has received speaker honoraria from Shire HGT and consultancy and speaker honoraria from Amicus, MyoKardia, Pfizer Inc., Sanofi Genzyme Idorsia and Alnylam.
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Altarescu G, Moore DF, Schiffmann R. Effect of genetic modifiers on cerebral lesions in Fabry disease. Neurology. 2005;64(12):2148–2150. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

