Molecular heterogeneity and CXorf67 alterations in posterior fossa group A (PFA) ependymomas
- PMID: 29909548
- PMCID: PMC6105278
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-018-1877-0
Molecular heterogeneity and CXorf67 alterations in posterior fossa group A (PFA) ependymomas
Abstract
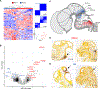
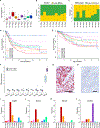
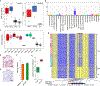
Of nine ependymoma molecular groups detected by DNA methylation profiling, the posterior fossa type A (PFA) is most prevalent. We used DNA methylation profiling to look for further molecular heterogeneity among 675 PFA ependymomas. Two major subgroups, PFA-1 and PFA-2, and nine minor subtypes were discovered. Transcriptome profiling suggested a distinct histogenesis for PFA-1 and PFA-2, but their clinical parameters were similar. In contrast, PFA subtypes differed with respect to age at diagnosis, gender ratio, outcome, and frequencies of genetic alterations. One subtype, PFA-1c, was enriched for 1q gain and had a relatively poor outcome, while patients with PFA-2c ependymomas showed an overall survival at 5 years of > 90%. Unlike other ependymomas, PFA-2c tumors express high levels of OTX2, a potential biomarker for this ependymoma subtype with a good prognosis. We also discovered recurrent mutations among PFA ependymomas. H3 K27M mutations were present in 4.2%, occurring only in PFA-1 tumors, and missense mutations in an uncharacterized gene, CXorf67, were found in 9.4% of PFA ependymomas, but not in other groups. We detected high levels of wildtype or mutant CXorf67 expression in all PFA subtypes except PFA-1f, which is enriched for H3 K27M mutations. PFA ependymomas are characterized by lack of H3 K27 trimethylation (H3 K27-me3), and we tested the hypothesis that CXorf67 binds to PRC2 and can modulate levels of H3 K27-me3. Immunoprecipitation/mass spectrometry detected EZH2, SUZ12, and EED, core components of the PRC2 complex, bound to CXorf67 in the Daoy cell line, which shows high levels of CXorf67 and no expression of H3 K27-me3. Enforced reduction of CXorf67 in Daoy cells restored H3 K27-me3 levels, while enforced expression of CXorf67 in HEK293T and neural stem cells reduced H3 K27-me3 levels. Our data suggest that heterogeneity among PFA ependymomas could have clinicopathologic utility and that CXorf67 may have a functional role in these tumors.
Keywords: CXorf67; DNA methylation profiling; Ependymoma; H3 K27-trimethylation; H3 K27M; Molecular heterogeneity; PRC2.
Figures


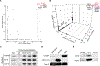
References
-
- Boulay G, Awad ME, Riggi N, Archer TC, Iyer S, Boonseng WE, et al. (2017) OTX2 Activity at Distal Regulatory Elements Shapes the Chromatin Landscape of Group 3 Medulloblastoma. Cancer discovery 7:288–301. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0844 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

