Squalene Synthase Deficiency: Clinical, Biochemical, and Molecular Characterization of a Defect in Cholesterol Biosynthesis
- PMID: 29909962
- PMCID: PMC6037199
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.05.004
Squalene Synthase Deficiency: Clinical, Biochemical, and Molecular Characterization of a Defect in Cholesterol Biosynthesis
Abstract
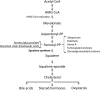
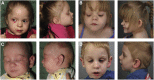
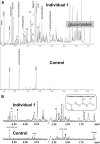
Mendelian disorders of cholesterol biosynthesis typically result in multi-system clinical phenotypes, underlining the importance of cholesterol in embryogenesis and development. FDFT1 encodes for an evolutionarily conserved enzyme, squalene synthase (SS, farnesyl-pyrophosphate farnesyl-transferase 1), which catalyzes the first committed step in cholesterol biosynthesis. We report three individuals with profound developmental delay, brain abnormalities, 2-3 syndactyly of the toes, and facial dysmorphisms, resembling Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome, the most common cholesterol biogenesis defect. The metabolite profile in plasma and urine suggested that their defect was at the level of squalene synthase. Whole-exome sequencing was used to identify recessive disease-causing variants in FDFT1. Functional characterization of one variant demonstrated a partial splicing defect and altered promoter and/or enhancer activity, reflecting essential mechanisms for regulating cholesterol biosynthesis/uptake in steady state.
Keywords: FDFT1; cholesterol biosynthesis; dysmorphism; syndactyly.
Crown Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Waterham H.R. Defects of cholesterol biosynthesis. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:5442–5449. - PubMed
-
- Schechter I., Conrad D.G., Hart I., Berger R.C., McKenzie T.L., Bleskan J., Patterson D. Localization of the squalene synthase gene (FDFT1) to human chromosome 8p22-p23.1. Genomics. 1994;20:116–118. - PubMed
-
- Do R., Kiss R.S., Gaudet D., Engert J.C. Squalene synthase: a critical enzyme in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway. Clin. Genet. 2009;75:19–29. - PubMed
-
- Jemal M., Ouyang Z. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometric method for quantitative determination in human urine of dicarboxylic (dioic) acids produced in the body as a consequence of cholesterol biosynthesis inhibition. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1998;709:233–241. - PubMed
-
- Vaidya S., Bostedor R., Kurtz M.M., Bergstrom J.D., Bansal V.S. Massive production of farnesol-derived dicarboxylic acids in mice treated with the squalene synthase inhibitor zaragozic acid A. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998;355:84–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

