Goal Format in Small-Sided Soccer Games: Technical Actions and Offensive Scenarios of Prepubescent Players
- PMID: 29910301
- PMCID: PMC5968898
- DOI: 10.3390/sports4040053
Goal Format in Small-Sided Soccer Games: Technical Actions and Offensive Scenarios of Prepubescent Players
Abstract
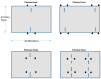
The aim of this study was to investigate the influence of the number of goal-posts and the positioning of goal-posts used within small-sided games on the frequency of technical actions and offensive scenarios performed by prepubescent players within soccer. The participants were eight male prepubescent soccer players (12.1 ± 0.5 years). The participants were video recorded for 20 min playing four different formats of 4v4 small-sided games: (1) standard two goal game; (2) four goal game, one goal in each corner; (3) two goal game with goal-posts positioned 9.14 m/10 yd infield, scoring only through the back of the goal; (4) four goal-game, one goal positioned 9.14 m/10 yd infield in each corner, scoring through either the front or back of each goal. Chi-squared tests of independence were utilized to statistically explore the impact of the different small-sided game formats. There were significant associations (p < 0.05) observed between the different small-sided game formats and the frequency of turns, dribbles, shots, goals and overlaps performed. For example, players performed more turns in small-sided game format two and more shots during small-sided game format four. It is suggested coaches should consider using a variation of the number and positioning of goal-posts in small-sided games as an effective training tool in the development of prepubescent soccer players. This will enable coaches to vary the focus of sessions, and develop specific technical and tactical actions within a situation similar to that of real match-play.
Keywords: performance analysis; player development; prepubescent soccer; tactical component; technical component.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gonzalez-Villora S., Garcia-Lopez L.M., Gutierrez-Diaz D., Pastor-Vicedo J.C. Tactical awareness, decision making and skill in youth soccer players (under-14 years) J. Hum. Sport Exerc. 2013;8:412–426. doi: 10.4100/jhse.2012.82.09. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources