Long-term safety of tiotropium/olodaterol Respimat® in patients with moderate-to-very severe COPD and renal impairment in the TONADO® studies
- PMID: 29910611
- PMCID: PMC5987861
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S161489
Long-term safety of tiotropium/olodaterol Respimat® in patients with moderate-to-very severe COPD and renal impairment in the TONADO® studies
Abstract
Introduction: The safety, lung function efficacy, and symptomatic benefits of combined tiotropium and olodaterol in patients with COPD were established in the 1-year TONADO® studies (NCT01431274; NCT01431287). As tiotropium is predominantly excreted by the kidneys, the long-term safety profile of tiotropium/olodaterol was investigated in patients with renal impairment in a prespecified safety analysis of the TONADO studies.
Methods: These were 2 replicate, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, 52-week Phase III studies that assessed tiotropium/olodaterol compared with tiotropium or olodaterol alone (all via Respimat®) in patients with moderate-to-very severe COPD. In this analysis, renal impairment was defined as mild (creatinine clearance [CLcr] 60-89 mL/min), moderate (CLcr 30-59 mL/min) or severe (CLcr 15-29 mL/min). Adverse events (AEs) were pooled from both studies.
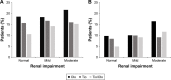
Results: Of 3,041 patients included in this analysis, 1,333 (43.8%) had mild, 404 (13.3%) had moderate, and 5 (0.2%) had severe renal impairment; these were distributed equally between treatment groups. Almost one-quarter of all treated patients (23.4%) had a history of cardiac disorder, 45.6% had hypertension, and 13.3% had glucose metabolism disorders, including diabetes. AEs with olodaterol, tiotropium, and tiotropium/olodaterol occurred in 75.1%, 70.8%, and 72.0% of patients with no renal impairment, 75.7%, 74.0%, and 73.3% with mild renal impairment, and 84.3%, 79.5%, and 79.7% with moderate renal impairment, respectively. There was no notable effect of renal impairment on the proportion of patients with an AE, and no differences were observed between tiotropium/olodaterol versus the monocomponents. There was no difference in the incidence of major adverse cardiac events, renal and urinary tract AEs, or potential anticholinergic effects with increasing severity of renal impairment.
Conclusion: Over half the patients enrolled in the TONADO studies had renal impairment, and there was a high level of pre-existing cardiovascular comorbidity. The safety and tolerability of tiotropium/olodaterol is comparable to the monocomponents, irrespective of the level of renal impairment.
Keywords: COPD; comorbidities; olodaterol; renal impairment; safety; tiotropium.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure RB reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Roche, and Teva, as well as grants to Mainz University from Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and Roche, outside the submitted work. ED’s clinical department has received financial support from Boehringer Ingelheim and Novartis to perform clinical studies; he has participated in advisory boards for Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Cipla, Novartis, and AstraZeneca, for which a fee was given (not related to this work); he has received travel grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, and AstraZeneca to attend international congresses and has received speaker’s fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, and Novartis. UB, IMK, and MT are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim International. CLF has received financial support from Boehringer Ingelheim to perform clinical studies. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Long-term general and cardiovascular safety of tiotropium/olodaterol in patients with moderate to very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Respir Med. 2017 Jan;122:58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2016.11.011. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Respir Med. 2017. PMID: 27993292 Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy and safety of combined tiotropium and olodaterol via the Respimat(®) inhaler in patients with COPD: results from the Japanese sub-population of the Tonado(®) studies.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016 Aug 29;11:2017-27. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S110389. eCollection 2016. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016. PMID: 27621608 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of tiotropium + olodaterol maintenance treatment in patients with COPD in the TONADO® and OTEMTO® studies: a subgroup analysis by age.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016 Oct 31;11:2701-2710. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S108758. eCollection 2016. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016. PMID: 27843306 Free PMC article.
-
Tiotropium/Olodaterol: A Review in COPD.Drugs. 2016 Jan;76(1):135-46. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0527-2. Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26683033 Review.
-
Olodaterol + tiotropium bromide for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2015;8(5):529-39. doi: 10.1586/17512433.2015.1075389. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26294073 Review.
Cited by
-
Major comorbidities lead to the risk of adverse cardiovascular events in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients using inhaled long-acting bronchodilators: a case-control study.BMC Pulm Med. 2019 Dec 3;19(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s12890-019-0999-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2019. PMID: 31795986 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term safety of tiotropium/olodaterol in older patients with moderate-to-very-severe COPD in the TONADO® studies.NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2020 Dec 4;30(1):53. doi: 10.1038/s41533-020-00212-w. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 33277507 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The once-daily fixed-dose combination of olodaterol and tiotropium in the management of COPD: current evidence and future prospects.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2019 Jan-Dec;13:1753466619843426. doi: 10.1177/1753466619843426. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2019. PMID: 31002020 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Chronic Respiratory Diseases. [Accessed June 8, 2017]. Available from: http://www.who.int/respiratory/copd/burden/en/
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: 2016 Report. [Accessed April 27, 2016]. Available from: http://goldcopd.org/global-strategy-diagnosis-management-prevention-copd...
-
- Tashkin DP, Celli B, Senn S, et al. A 4-year trial of tiotropium in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(15):1543–1554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

