Adaptive Regulation of Osteopontin Production by Dendritic Cells Through the Bidirectional Interaction With Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
- PMID: 29910810
- PMCID: PMC5992779
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01207
Adaptive Regulation of Osteopontin Production by Dendritic Cells Through the Bidirectional Interaction With Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
Abstract
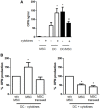
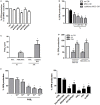
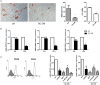
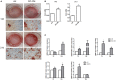
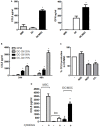
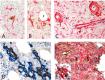
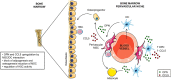
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) exert immunosuppressive effects on immune cells including dendritic cells (DCs). However, many details of the bidirectional interaction of MSCs with DCs are still unsolved and information on key molecules by which DCs can modulate MSC functions is limited. Here, we report that osteopontin (OPN), a cytokine involved in homeostatic and pathophysiologic responses, is constitutively expressed by DCs and regulated in the DC/MSC cocultures depending on the activation state of MSCs. Resting MSCs promoted OPN production, whereas the production of OPN was suppressed when MSCs were activated by proinflammatory cytokines (i.e., TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β). OPN induction required cell-to-cell contact, mediated at least in part, by β1 integrin (CD29). Conversely, activated MSCs inhibited the release of OPN via the production of soluble factors with a major role played by Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). Accordingly, pretreatment with indomethacin significantly abrogated the MSC-mediated suppression of OPN while the direct addition of exogenous PGE2 inhibited OPN production by DCs. Furthermore, DC-conditioned medium promoted osteogenic differentiation of MSCs with a concomitant inhibition of adipogenesis. These effects were paralleled by the repression of the adipogenic markers PPARγ, adiponectin, and FABP4, and induction of the osteogenic markers alkaline phosphatase, RUNX2, and of the bone-anabolic chemokine CCL5. Notably, blocking OPN activity with RGD peptides or with an antibody against CD29, one of the OPN receptors, prevented the effects of DC-conditioned medium on MSC differentiation and CCL5 induction. Because MSCs have a key role in maintenance of bone marrow (BM) hematopoietic stem cell niche through reciprocal regulation with immune cells, we investigated the possible MSC/DC interaction in human BM by immunohistochemistry. Although DCs (CD1c+) are a small percentage of BM cells, we demonstrated colocalization of CD271+ MSCs with CD1c+ DCs in normal and myelodysplastic BM. OPN reactivity was observed in occasional CD1c+ cells in the proximity of CD271+ MSCs. Altogether, these results candidate OPN as a signal modulated by MSCs according to their activation status and involved in DC regulation of MSC differentiation.
Keywords: adipogenesis; ccl5; dendritic cells; mesenchymal stromal cells; osteogenesis; osteopontin.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

