Predicting the DNP-SENS efficiency in reactive heterogeneous catalysts from hydrophilicity
- PMID: 29910939
- PMCID: PMC5982197
- DOI: 10.1039/c8sc00532j
Predicting the DNP-SENS efficiency in reactive heterogeneous catalysts from hydrophilicity
Abstract
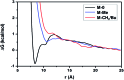
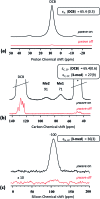
Identification of surfaces at the molecular level has benefited from progress in dynamic nuclear polarization surface enhanced NMR spectroscopy (DNP SENS). However, the technique is limited when using highly sensitive heterogeneous catalysts due to secondary reaction of surface organometallic fragments (SOMFs) with stable radical polarization agents. Here, we observe that in non-porous silica nanoparticles (NPs) (dparticle = 15 nm) some DNP enhanced NMR or SENS characterizations are possible, depending on the metal-loading of the SOMF and the type of SOMF substituents (methyl, isobutyl, neopentyl). This unexpected observation suggests that aggregation of the nanoparticles occurs in non-polar solvents (such as ortho-dichlorobenzene) leading to (partial) protection of the SOMF inside the interparticle space, thereby preventing reaction with bulky polarization agents. We discover that the DNP SENS efficiency is correlated with the hydrophilicity of the SOMF/support, which depends on the carbon and SOMF concentration. Nitrogen sorption measurements to determine the BET constant (CBET) were performed. This constant allows us to predict the aggregation of silica nanoparticles and consequently the efficiency of DNP SENS. Under optimal conditions, CBET > 60, we found signal enhancement factors of up to 30.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Formulation Protocol with Pyridine to Enable Dynamic Nuclear Polarization Surface-Enhanced NMR Spectroscopy on Reactive Surface Sites: Case Study with Olefin Polymerization and Metathesis Catalysts.J Phys Chem Lett. 2020 May 7;11(9):3401-3407. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c00716. Epub 2020 Apr 17. J Phys Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32271018
-
Dynamic nuclear polarization surface enhanced NMR spectroscopy.Acc Chem Res. 2013 Sep 17;46(9):1942-51. doi: 10.1021/ar300322x. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Acc Chem Res. 2013. PMID: 23517009
-
Dendritic polarizing agents for DNP SENS.Chem Sci. 2017 Jan 1;8(1):416-422. doi: 10.1039/c6sc03139k. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Chem Sci. 2017. PMID: 28451187 Free PMC article.
-
Is solid-state NMR enhanced by dynamic nuclear polarization?Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2015 Apr-May;66-67:6-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2015.01.003. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2015. PMID: 25779337 Review.
-
Recent developments in MAS DNP-NMR of materials.Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2019 Sep;101:116-143. doi: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2019.05.009. Epub 2019 May 27. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2019. PMID: 31189121 Review.
Cited by
-
Small Molecules, Non-Covalent Interactions, and Confinement.Molecules. 2020 Jul 21;25(14):3311. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143311. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32708283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spin Hyperpolarization in Modern Magnetic Resonance.Chem Rev. 2023 Feb 22;123(4):1417-1551. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00534. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Chem Rev. 2023. PMID: 36701528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Nuclear Polarization Using 3D Aromatic Boron Cluster Radicals.J Phys Chem Lett. 2021 Jan 14;12(1):13-18. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c03216. Epub 2020 Dec 9. J Phys Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 33296205 Free PMC article.
-
Polarizing agents for efficient high field DNP solid-state NMR spectroscopy under magic-angle spinning: from design principles to formulation strategies.Chem Sci. 2023 May 12;14(23):6120-6148. doi: 10.1039/d3sc01079a. eCollection 2023 Jun 14. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 37325158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface enhanced dynamic nuclear polarization solid-state NMR spectroscopy sheds light on Brønsted-Lewis acid synergy during the zeolite catalyzed methanol-to-hydrocarbon process.Chem Sci. 2019 Aug 21;10(39):8946-8954. doi: 10.1039/c9sc02215e. eCollection 2019 Oct 21. Chem Sci. 2019. PMID: 32190235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pelletier J. D. A., Basset J.-M. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016;49:664–677. - PubMed
-
- Li C. and Liu Y., Bridging Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Catalysis: Concepts, Strategies, and Applications, Wiley, 2014.
-
- Conley M. P., Rossini A. J., Comas-Vives A., Valla M., Casano G., Ouari O., Tordo P., Lesage A., Emsley L., Coperet C. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014;16:17822–17827. - PubMed
-
- Trewyn B., Heterogeneous Catalysis for Today's Challenges: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications, Royal Society of Chemistry, 2015.
-
- Coperet C., Chabanas M., Saint-Arroman R. P., Basset J. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2003;42:156–181. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

