Combined Biomarkers Predict Acute Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients With Suspected Sepsis
- PMID: 29912095
- PMCID: PMC6010038
- DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003137
Combined Biomarkers Predict Acute Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients With Suspected Sepsis
Abstract
Objectives: Sepsis is associated with high early and total in-hospital mortality. Despite recent revisions in the diagnostic criteria for sepsis that sought to improve predictive validity for mortality, it remains difficult to identify patients at greatest risk of death. We compared the utility of nine biomarkers to predict mortality in subjects with clinically suspected bacterial sepsis.
Design: Cohort study.
Setting: The medical and surgical ICUs at an academic medical center.
Subjects: We enrolled 139 subjects who met two or more systemic inflammatory response syndrome (systemic inflammatory response syndrome) criteria and received new broad-spectrum antibacterial therapy.
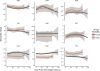
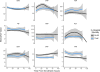
Interventions: We assayed nine biomarkers (α-2 macroglobulin, C-reactive protein, ferritin, fibrinogen, haptoglobin, procalcitonin, serum amyloid A, serum amyloid P, and tissue plasminogen activator) at onset of suspected sepsis and 24, 48, and 72 hours thereafter. We compared biomarkers between groups based on both 14-day and total in-hospital mortality and evaluated the predictive validity of single and paired biomarkers via area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.
Measurements and main results: Fourteen-day mortality was 12.9%, and total in-hospital mortality was 29.5%. Serum amyloid P was significantly lower (4/4 timepoints) and tissue plasminogen activator significantly higher (3/4 timepoints) in the 14-day mortality group, and the same pattern held for total in-hospital mortality (Wilcoxon p ≤ 0.046 for all timepoints). Serum amyloid P and tissue plasminogen activator demonstrated the best individual predictive performance for mortality, and combinations of biomarkers including serum amyloid P and tissue plasminogen activator achieved greater predictive performance (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve > 0.76 for 14-d and 0.74 for total mortality).
Conclusions: Combined biomarkers predict risk for 14-day and total mortality among subjects with suspected sepsis. Serum amyloid P and tissue plasminogen activator demonstrated the best discriminatory ability in this cohort.
Conflict of interest statement
The remaining authors have disclosed that they do not have any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Sepsis Biomarkers…The Long and Winding Road.Crit Care Med. 2018 Jul;46(7):1194-1195. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003166. Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 29912103 No abstract available.
-
Is Combined Biomarkers a Future Tool for Early Prediction of Mortality Among Septic Patients?Crit Care Med. 2019 Mar;47(3):e275. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003456. Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 30768527 No abstract available.
-
The authors reply.Crit Care Med. 2019 Mar;47(3):e275-e276. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003587. Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 30768528 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vincent J-L, Marshall JC, Namendys-Silva SA, et al. Assessment of the worldwide burden of critical illness: the intensive care over nations (ICON) audit. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2:380–386. - PubMed
-
- Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NKJ, et al. Assessment of Global Incidence and Mortality of Hospital-treated Sepsis. Current Estimates and Limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193:259–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

