Vasodilator Activity of Compounds Isolated from Plants Used in Mexican Traditional Medicine
- PMID: 29912156
- PMCID: PMC6100030
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23061474
Vasodilator Activity of Compounds Isolated from Plants Used in Mexican Traditional Medicine
Abstract
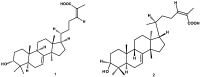
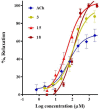
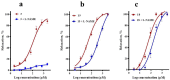
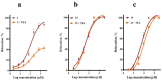
Arterial hypertension is one of the main risk factors in the development of cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, it is important to look for new drugs to treat hypertension. In this study, we carried out the screening of 19 compounds (triterpenes, diterpenes, sesquiterpenes, lignans, and flavonoids) isolated from 10 plants used in Mexican traditional medicine to determine whether they elicited vascular smooth muscle relaxation and, therefore, could represent novel anti-hypertension drug candidates. The vasorelaxant activity of these compounds was evaluated on the isolated rat aorta assay and the results obtained from this evaluation showed that three compounds induced a significant vasodilatory effect: meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid [half maximal effective concentration (EC50), 49.9 ± 11.2 µM; maximum effect (Emax), 99.8 ± 2.7%]; corosolic acid (EC50, 108.9 ± 6.7 µM; Emax, 96.4 ± 4.2%); and 5,8,4′-trihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone (EC50, 122.3 ± 7.6 µM; Emax, 99.5 ± 5.4%). Subsequently, involvement of the NO/cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) and H₂S/ATP-sensitive potassium channel (KATP) pathways on the vasodilator activity of these compounds was assessed. The results derived from this analysis showed that the activation of both pathways contributes to the vasorelaxant effect of corosolic acid. On the other hand, the vasodilator effect of meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid and 5,8,4′-trihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone, partly involves stimulation of the NO/cGMP pathway. However, these compounds also showed an important endothelium-independent vasorelaxant effect, whose mechanism of action remains to be clarified. This study indicates that meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid, corosolic acid, and 5,8,4′-trihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone could be used as lead compounds for the synthesis of new derivatives with a higher potency to be developed as drugs for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: 5,8,4′-trihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone; corosolic acid; meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid hydrogen sulfide; nitric oxide; vasorelaxation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Vasorelaxant effects of Cerebralcare Granule® are mediated by NO/cGMP pathway, potassium channel opening and calcium channel blockade in isolated rat thoracic aorta.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Aug 8;155(1):572-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.05.062. Epub 2014 Jun 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24924524
-
Pentacyclic triterpenoids and ceramide mediate the vasorelaxant activity of Vitex cienkowskii via involvement of NO/cGMP pathway in isolated rat aortic rings.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Jan 7;133(1):204-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.09.033. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20920567
-
Vasorelaxant effects of Shunaoxin pill are mediated by NO/cGMP pathway, HO/CO pathway and calcium channel blockade in isolated rat thoracic aorta.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Sep 15;173:352-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.07.048. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26239154
-
Vasodilator compounds derived from plants and their mechanisms of action.Molecules. 2013 May 17;18(5):5814-57. doi: 10.3390/molecules18055814. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 23685938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secondary Metabolites of Plants as Modulators of Endothelium Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 3;22(5):2533. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052533. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33802468 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
State-of-the-Art and Opportunities for Bioactive Pentacyclic Triterpenes from Native Mexican Plants.Plants (Basel). 2022 Aug 23;11(17):2184. doi: 10.3390/plants11172184. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36079566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro examination of anti-parasitic, anti-Alzheimer, insecticidal and cytotoxic potential of Ajuga bracteosa Wallich leaves extracts.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 May;28(5):3031-3036. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.02.044. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34025179 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a quantified herbal extract of hawthorn Crataegus mexicana leaves with vasodilator effect.Saudi Pharm J. 2021 Nov;29(11):1258-1266. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2021.10.002. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Saudi Pharm J. 2021. PMID: 34819787 Free PMC article.
-
Marjoram Relaxes Rat Thoracic Aorta Via a PI3-K/eNOS/cGMP Pathway.Biomolecules. 2019 Jun 11;9(6):227. doi: 10.3390/biom9060227. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31212721 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Chemical Composition and the Biological Activities of Vitis vinifera Stem Extracts.Molecules. 2022 May 12;27(10):3109. doi: 10.3390/molecules27103109. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35630586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prospective Studies Collaboration Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: A meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet. 2002;360:1903–1913. - PubMed
-
- Rapsomaniki E., Timmis A., George J., Pujades-Rodriguez M., Shah A.D., Denaxas S., White I.R., Caulfield M.J., Deanfield J.E., Smeeth L. Blood pressure and incidence of twelve cardiovascular diseases: Lifetime risks, healthy life-years lost, and age-specific associations in 1.25 million people. Lancet. 2014;383:1899–1911. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60685-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu F., Guo Y., Chatterji S., Zheng Y., Naidoo N., Jiang Y., Biritwum R., Yawson A., Minicuci N., Salinas-Rodriguez A. Common risk factors for chronic non-communicable diseases among older adults in China, Ghana, Mexico, India, Russia and South Africa: The study on global AGEing and adult health (SAGE) wave 1. BMC Public Health. 2015;15:88. doi: 10.1186/s12889-015-1407-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization The Top Ten Causes of Death. [(accessed on 17 February 2017)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

