Chronic stress-associated visceral hyperalgesia correlates with severity of intestinal barrier dysfunction
- PMID: 29912860
- PMCID: PMC6097612
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001271
Chronic stress-associated visceral hyperalgesia correlates with severity of intestinal barrier dysfunction
Abstract
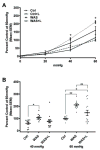
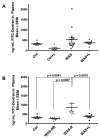
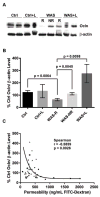
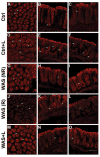
In humans, chronic psychological stress is associated with increased intestinal paracellular permeability and visceral hyperalgesia, which is recapitulated in the chronic intermittent water avoidance stress (WAS) rat model. However, it is unknown whether enhanced visceral pain and permeability are intrinsically linked and correlate. Treatment of rats with lubiprostone during WAS significantly reduced WAS-induced changes in intestinal epithelial paracellular permeability and visceral hyperalgesia in a subpopulation of rats. Lubiprostone also prevented WAS-induced decreases in the epithelial tight junction protein, occludin (Ocln). To address the question of whether the magnitude of visceral pain correlates with the extent of altered intestinal permeability, we measured both end points in the same animal because of well-described individual differences in pain response. Our studies demonstrate that visceral pain and increased colon permeability positively correlate (0.6008, P = 0.0084). Finally, exposure of the distal colon in control animals to Ocln siRNA in vivo revealed that knockdown of Ocln protein inversely correlated with increased paracellular permeability and enhanced visceral pain similar to the levels observed in WAS-responsive rats. These data support that Ocln plays a potentially significant role in the development of stress-induced increased colon permeability. We believe this is the first demonstration that the level of chronic stress-associated visceral hyperalgesia directly correlates with the magnitude of altered colon epithelial paracellular permeability.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chronic stress and intestinal permeability: Lubiprostone regulates glucocorticoid receptor-mediated changes in colon epithelial tight junction proteins, barrier function, and visceral pain in the rodent and human.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019 Feb;31(2):e13477. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13477. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019. PMID: 30284340 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H3K9 methylation regulates chronic stress and IL-6-induced colon epithelial permeability and visceral pain.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020 Dec;32(12):e13941. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13941. Epub 2020 Aug 2. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020. PMID: 32743845 Free PMC article.
-
Multispecies probiotic protects gut barrier function in experimental models.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jun 14;20(22):6832-43. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i22.6832. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24944474 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Epigenomic Regulatory Pathways in the Gut-Brain Axis and Visceral Hyperalgesia.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Mar;42(2):361-376. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01108-0. Epub 2021 May 31. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 34057682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of lactobacilli on paracellular permeability in the gut.Nutrients. 2011 Jan;3(1):104-17. doi: 10.3390/nu3010104. Epub 2011 Jan 12. Nutrients. 2011. PMID: 22254077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sex differences in visceral sensitivity and brain activity in a rat model of comorbid pain: a longitudinal study.Pain. 2024 Mar 1;165(3):698-706. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003074. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Pain. 2024. PMID: 37756658 Free PMC article.
-
Early and Late Transcriptional Changes in Blood, Neural, and Colon Tissues in Rat Models of Stress-Induced and Comorbid Pain Hypersensitivity Reveal Regulatory Roles in Neurological Disease.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2022 May 17;3:886042. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2022.886042. eCollection 2022. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35655748 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility and acceptability of an adapted environmental enrichment intervention for endometriosis: A pilot study.Front Glob Womens Health. 2023 Jan 4;3:1058559. doi: 10.3389/fgwh.2022.1058559. eCollection 2022. Front Glob Womens Health. 2023. PMID: 36683601 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral mechanisms contribute to comorbid visceral hypersensitivity induced by preexisting orofacial pain and stress in female rats.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020 Jul;32(7):e13833. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13833. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020. PMID: 32155308 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-dependent alterations of colonic epithelial permeability: relevance to irritable bowel syndrome.Front Physiol. 2025 Feb 21;16:1509935. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1509935. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40061455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilera M, Vergara P, Martinez V. Stress and antibiotics alter luminal and wall-adhered microbiota and enhance the local expression of visceral sensory-related systems in mice. Neurogastroenterology and motility : the official journal of the European Gastrointestinal Motility Society. 2013;25(8):e515–529. - PubMed
-
- Ait-Belgnaoui A, Bradesi S, Fioramonti J, Theodorou V, Bueno L. Acute stress-induced hypersensitivity to colonic distension depends upon increase in paracellular permeability: role of myosin light chain kinase. Pain. 2005;113(1–2):141–147. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

